Critical values for dimensional parameters of mesotheliomagenic mineral fibers: evidence from the dimensions and rigidity of MWCNT
- PMID: 40330553
- PMCID: PMC12052570
- DOI: 10.3389/ftox.2025.1568513
Critical values for dimensional parameters of mesotheliomagenic mineral fibers: evidence from the dimensions and rigidity of MWCNT
Abstract
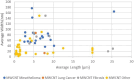
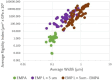
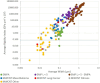
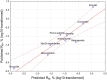
MWCNT (multi-walled carbon nanotubes) used in 72 animal instillation or inhalation studies were classified by average length, average width, Young's modulus, Rigidity Index (RI), and potency for mesothelioma in animals. The RI is based on the Euler buckling theory. MWCNT that induce mesothelioma have average lengths >2 µm and widths >37 nm, and average RI > 0.05 (µm2 x GPa x 104). Many noncarcinogenic MWCNT materials have RI < 0.05 and lack biological rigidity. In comparison, Elongate Mineral Particle (EMP) populations with one exception have RI > 0.05. Mineral particles likely to have RI < 0.05 include chrysotile fibrils with lengths >5 μm, amosite and crocidolite fibers with widths <60 nm, and sheet silicate fibers with widths <200 nm. The product of percent EMPA, average RI, and biosolubility among silicates correlates with known mesothelioma potency. The derived models reproduce published values of RM with high statistical significance (P < 0.05). Average RI, length, and width are critical parameters for mesotheliomagenicity for both MWCNT and EMPA mineral fiber.
Keywords: EMP; EMPA; asbestos; carbon nanotubes; cleavage fragments; mesothelioma; rigidity.
Copyright © 2025 Wylie and Korchevskiy.
Conflict of interest statement
Author AK was employed by Chemistry & Industrial Hygiene, Inc. The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Augustine R., Hasan A., Primavera R., Wilson R. J., Thakor A. S., Kevadiya B. D. (2020). Cellular uptake and retention of nanoparticles: insights on particle properties and interaction with cellular components. Mat. Today Commun. 25, 101692. 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.101692 - DOI
-
- Aveston A. (1969). The mechanical properties of asbestos. J. Mater Sci. 4 (4), 625–633. 10.1007/BF00550118 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

