The Predictive Value of Melatonin Levels for the Development of Diabetic Nephropathy in Men with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 40330571
- PMCID: PMC12050062
- DOI: 10.61186/rbmb.13.3.341
The Predictive Value of Melatonin Levels for the Development of Diabetic Nephropathy in Men with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
Background: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) poses a significant public health challenge due to its high prevalence. Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is one of the most severe complications associated with T2DM. Early prediction of DN in patients with T2DM can significantly aid in managing this disease. This study takes an approach by investigating the potential role of melatonin and thyroid hormone levels as predictive biomarkers for the progression of diabetic nephropathy in individuals diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
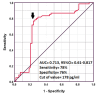
Methods: Our cross-sectional study involved 120 male participants, divided into two groups: 60 patients with T2DM and 60 with DN. The Cobas technique was used to measure serum thyroid hormone levels and quantified melatonin levels using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). A receiver utilizing characteristic (ROC) curve analysis to evaluate the predictive value of serum melatonin for DN was performed.
Results: No notable disparities in thyroid function tests were observed between diabetic patients with and without DN. However, the average serum melatonin quantity in patients with DN. (177.25 ± 60.48 pg/mL) was drastically lower in those with T2DM without DN (199.9 ± 55.16 pg/mL). The sensitivity and specificity of melatonin in predicting DN were 78% and 76%, respectively, with an optimal cut-off value of 178 pg/mL.
Conclusions: Serum melatonin levels exhibited a notable reduction. among individuals who were diabetic with DN, suggesting its potential utility as an additional predictive marker for developing DN in patients with T2DM.
Keywords: Diabetes Mellitus; Diabetic Nephropathy; Melatonin; Thyroid Activity Tests.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Thyroid stimulating hormone and free triiodothyronine are valuable predictors for diabetic nephropathy in patient with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Ann Transl Med. 2018 Aug;6(15):305. doi: 10.21037/atm.2018.07.07. Ann Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 30211193 Free PMC article.
-
Immunological insights into role of Th9 and Treg cell homeostasis and cytokines dynamics in the progression of diabetic nephropathy.Int Rev Immunol. 2025 Jun 12:1-25. doi: 10.1080/08830185.2025.2515836. Online ahead of print. Int Rev Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40501365
-
Association of Thyroid Autoantibodies with Diabetic Nephropathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients.Altern Ther Health Med. 2024 Dec;30(12):374-380. Altern Ther Health Med. 2024. PMID: 38518164
-
Diagnostic Accuracy of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin for Predicting Early Diabetic Nephropathy in Patients with Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.J Appl Lab Med. 2019 Jul;4(1):78-94. doi: 10.1373/jalm.2018.028530. Epub 2019 Mar 1. J Appl Lab Med. 2019. PMID: 31639710
-
Review of early circulating biomolecules associated with diabetes nephropathy - Ideal candidates for early biomarker array test for DN.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2021 Dec;182:109122. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109122. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2021. PMID: 34742785 Review.
Cited by
-
Palmitate-increased TGF-β1 Gene Expression and p-Smad2/3 Protein Levels Attenuated by Chicoric Acid in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2025 Jan;13(4):540-548. doi: 10.61186/rbmb.13.4.540. Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40842890 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Roglic G. WHO Global report on diabetes: A summary. Int J Noncommunicable Dis. 2016;1(1):3–8.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
