Unraveling the Genetic and Environmental Risk Factors of Autism Spectrum Disorder Through a Case-Control Study in Armenia
- PMID: 40330750
- PMCID: PMC12050264
- DOI: 10.1002/hsr2.70801
Unraveling the Genetic and Environmental Risk Factors of Autism Spectrum Disorder Through a Case-Control Study in Armenia
Abstract
Background and aims: Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is influenced by genetic and environmental factors. This study investigates genetic mutations and prenatal factors associated with ASD, including their interplay, in a multicenter case-control study.
Methods: The study included 297 participants (149 ASD cases, 148 controls). Genetic data were analyzed using Multiplex Ligation-dependent Probe Amplification (MLPA) for ASD-associated chromosomal regions. Environmental data covered prenatal, perinatal, and neonatal factors. Logistic regression and stratified analyses were performed.
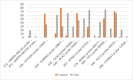
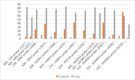
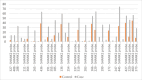
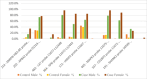
Results: Significant associations were found between ASD and mutations in 15q11-15q13, 16p11, and 11q13 regions, particularly in SHANK2 and SHANK3. Females with ASD showed higher mutation rates than males. Prenatal factors (e.g., MgB6 use, labor-inducing drugs, maternal stress, pregnancy complications, shorter interpregnancy intervals) exacerbated ASD risk when combined with specific genetic variations. Duphaston use during pregnancy, alongside certain mutations, may influence ASD risk, potentially offering protective effects.
Conclusion: This study highlights the importance of integrating genetic and environmental factors in ASD research. Findings underscore the need for tailored early interventions, prenatal care advice, and genetic counseling for at-risk families. Future studies should validate these findings in larger, diverse populations and explore underlying mechanisms.
Keywords: autism spectrum disorder; case–control study; genetics; gene‐environment; pregnancy.
© 2025 The Author(s). Health Science Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A case-control study on pre-, peri-, and neonatal risk factors associated with autism spectrum disorder among Armenian children.Sci Rep. 2024 May 29;14(1):12308. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-63240-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38811666 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating heterogeneity in ASD symptomatology, cognitive ability, and adaptive functioning among 16p11.2 CNV carriers.Autism Res. 2020 Aug;13(8):1300-1310. doi: 10.1002/aur.2332. Epub 2020 Jun 28. Autism Res. 2020. PMID: 32597026
-
Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification as a screening test in children with autism spectrum disorders.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2020 Jan;29(1):101-106. doi: 10.17219/acem/112609. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2020. PMID: 31990460
-
Autism spectrum disorder: neuropathology and animal models.Acta Neuropathol. 2017 Oct;134(4):537-566. doi: 10.1007/s00401-017-1736-4. Epub 2017 Jun 5. Acta Neuropathol. 2017. PMID: 28584888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The genetics of autism.Pediatrics. 2004 May;113(5):e472-86. doi: 10.1542/peds.113.5.e472. Pediatrics. 2004. PMID: 15121991 Review.
References
-
- West E. A., Travers J. C., Kemper T. D., et al., “Racial and Ethnic Diversity of Participants in Research Supporting Evidence‐Based Practices for Learners With Autism Spectrum Disorder,” Journal of Special Education 50, no. 3 (2016): 151–163, 10.1177/0022466916632495. - DOI
-
- “Data and Statistics on Autism Spectrum Disorder,” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), January 10, 2024, https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/autism/data.html.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

