Trauma-induced recurrent of scalp dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: a case report with a 6-year follow-up and literature review
- PMID: 40330930
- PMCID: PMC12053716
- DOI: 10.21037/acr-24-187
Trauma-induced recurrent of scalp dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: a case report with a 6-year follow-up and literature review
Abstract
Background: Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) is a rare mesenchymal cell-derived soft tissue tumor, especially on the scalp. As a result, there is a lack of insight into the etiology of its occurrence and the triggers of its recurrence, which makes diagnosis difficult. This paper reports a case with a long follow-up period in an attempt to provide some valuable evidence-based medicine to assist in the clinical work-up of diagnostic.
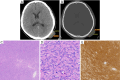
Case description: We selected a young male who underwent surgical treatment in our hospital in 2013, and his pathological result at that time was "suspected dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans". At the same time, we followed the patient for 6 years and performed a literature review on the current management of DFSP. Six years later, the patient's scalp mass recurred after a head trauma. Based on the patient's medical history and pathogenesis of the disease, we believe that the patient's disease may be related to trauma.
Conclusions: DFSP is rare in clinic, and it is easy to be misdiagnosed because of its atypical clinical symptoms and long diagnosis time. This article analyzed the case which has a long-time follow-up and reviewed the literature on DFSP. Therefore, this paper finds that trauma may be a causative factor in the development and recurrence, and provides a basis for evidence-based medicine for the diagnosis and treatment of this disease.
Keywords: Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP); case report; pathogenesis; recurrence; trauma.
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://acr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/acr-24-187/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
From Morphea to Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2022 Sep;30(2):113-115. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2022. PMID: 36254545
-
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: a report on 29 patients treated by Mohs micrographic surgery with long-term follow-up and review of the literature.Cancer. 2004 Jul 1;101(1):28-38. doi: 10.1002/cncr.20316. Cancer. 2004. PMID: 15221986
-
Report of two cases of recurrent scalp dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans and literature review.Indian J Dermatol. 2014 Nov;59(6):602-5. doi: 10.4103/0019-5154.143536. Indian J Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 25484394 Free PMC article.
-
Fine-needle aspiration of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans metastasizing to hemithorax with superior vena cava compression: Case report and literature review.Diagn Cytopathol. 2019 Aug;47(8):797-802. doi: 10.1002/dc.24179. Epub 2019 Mar 27. Diagn Cytopathol. 2019. PMID: 30919592 Review.
-
Malignancy arising within cutaneous tattoos: case of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans and review of literature.J Drugs Dermatol. 2011 Aug;10(8):837-42. J Drugs Dermatol. 2011. PMID: 21818504 Review.
References
-
- Darier J. Dermatofibromes progressifs et recidivants ou fibrosarcomes de la peau. Ann Dermatol Venereol 1924;5:545-62.
-
- Stamatakos M, Fyllos A, Siafogianni A, et al. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: a rare entity and review of the literature. J BUON 2014;19:34-41. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
