Evaluation of the Toxicity Profile and Central Nervous System Activities of Glue (Adhesive) Inhalation in Wistar Rats
- PMID: 40331057
- PMCID: PMC12052445
- DOI: 10.1155/jt/5535209
Evaluation of the Toxicity Profile and Central Nervous System Activities of Glue (Adhesive) Inhalation in Wistar Rats
Abstract
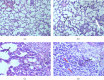
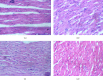
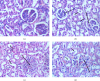
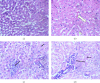
Background: Glue inhalation is a common unconventional substance of abuse, and it contains neurotoxic and volatile solvents. We examined the toxicity profile and central nervous system (CNS) activities of glue inhalation in Wistar rats. Methods: Acute toxicity was investigated, and the subacute toxicity was studied using 24 male Wistar rats at graded concentrations of air, 2, 4 and 8 mL glue (n = 6/group) for 28 days. Blood samples were collected for biochemical and haematological evaluations, and vital organs (lung, liver, kidney, heart, brain and eye) were used for histological analysis. Behavioural studies were carried out using an elevated plus maze, hole board test, open-field test, tail suspension test and forced swim test. Dependence and abstinence effects were also evaluated. Results: The lethal dose (LD50) of the inhalational glue was 14.14 mL. Glue significantly increased liver function parameters such as TB, DB, ALP, ALT, TP and electrolyte levels (K+ and HCO3) but reduced cholesterol levels in exposed rats. Glue inhalation had significant anxiolytic and depressant effects on the rats at concentrations of 4 and 8 mL. Histological analysis revealed liver and lung tissue abnormalities and subconjunctival inflammation in eye tissue at 8 mL. Conclusion: The study therefore suggests that glue inhalation has anxiolytic and depressant effects in Wistar rats.
Keywords: behaviour; central nervous system; depression; glue; toxicity.
Copyright © 2025 Abdulgafar Olayiwola Jimoh et al. Journal of Toxicology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Safety assessment of the aqueous extract of the flowers of Nymphaea lotus Linn (Nymphaeaceae): Acute, neuro- and subchronic oral toxicity studies in albinos Wistar rats.J Complement Integr Med. 2017 Mar 24;14(2):/j/jcim.2017.14.issue-2/jcim-2016-0046/jcim-2016-0046.xml. doi: 10.1515/jcim-2016-0046. J Complement Integr Med. 2017. PMID: 28291734
-
Toxicology and carcinogenesis studies of 1-bromopropane (CAS No. 106-94-5) in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice (inhalation studies).Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 2011 Aug;(564):1-190. Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 2011. PMID: 21921963
-
Toxicological evaluation of the aqueous whole plant extract of Aerva lanata (l.) Juss. ex Schult (Amaranthaceae).J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Aug 17;208:174-184. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.06.032. Epub 2017 Jun 28. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28668647
-
Volatile substance abuse.Bull Narc. 1994;46(2):49-78. Bull Narc. 1994. PMID: 7866398 Review.
-
Medical complications of glue sniffing.South Med J. 1996 May;89(5):455-62. doi: 10.1097/00007611-199605000-00001. South Med J. 1996. PMID: 8638168 Review.
References
-
- Danjuma A., Ibrahim Taiwo A., Omoniyi S. O. Nonconventional Use of Substances Among Youth in Nigeria: Viewpoints of Students in a Nigerian Tertiary Institution. Journal of Nursing & Care . 2015;04(06) doi: 10.4172/2167-1168.1000311. - DOI
-
- Jimoh A. O., Ibeabuchi O. E., Abubakar B., et al. Evaluation of the Toxicity Profile and Central Nervous System (CNS) Activities of Glue (Adhesive) Inhalation in Wistar Rats. 2023.
-
- Egbuonu A. C., Egbuonu O. N., Samuel E. S. The Prevalence of Some Psychoactive Substances Use Among Secondary School Adolescents in Bosso Local Government Area, Nigeria. Journal of Environmental Toxicology and Public Health . 2015;1(1):6–10.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

