Metabolic effects of late-onset estradiol replacement in high-fat-fed ovariectomized mice
- PMID: 40331103
- PMCID: PMC12051062
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crphys.2025.100144
Metabolic effects of late-onset estradiol replacement in high-fat-fed ovariectomized mice
Abstract
Background: Decreased estrogen levels in postmenopausal women negatively impact metabolic health. It is known that estradiol (E2) replacement can reverse this condition. However, there is no consensus on whether the effects mediated by E2 depend on the starting time of E2 replacement after menopause. We aimed to investigate the effects of different onset E2 treatments on glucose tolerance and metabolic parameters in high-fat-fed ovariectomized mice.
Material and methods: Eight-week-old female C57BL/6J mice were divided into three groups: SHAM, OVX, and E2, to evaluate three different time points of E2 replacement after ovariectomy: early (after 4 weeks), intermediate (after 12 weeks), and late replacement (after 20 weeks). E2 groups received treatment through subcutaneous pellets.
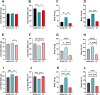
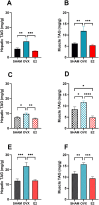
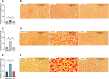
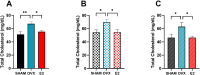
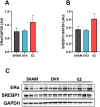
Results: E2 replacement improved the parameters analyzed independently of the time since ovariectomy, reducing body weight gain and fat mass, as well as increasing the percentage of lean mass. Glucose intolerance, fasting insulin, HOMA-IR, and cholesterol levels were also reduced after treatment with E2. In the liver, there was a decrease in triacylglycerol (TAG) deposition, with no difference in the expression of SREBP1 and ERα proteins. In the muscle, there was a decrease in TAG deposition. In periuterine adipose tissue, there was an increase in the expression of SREBP1, FASN, and SCD, with no difference in the expression of ERα.
Conclusions: Our findings reinforce the critical role of E2 in regulating both glucose and lipid metabolism and indicate that E2 action on metabolic health was not dependent on time since ovariectomy for the parameters analyzed.
Keywords: Estradiol replacement; Insulin resistance; Lipid metabolism; Menopause; Ovariectomy.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effect of ovariectomy on adipose tissue of mice in the absence of estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha): a potential role for estrogen receptor beta (ERbeta).Horm Metab Res. 2002 Nov-Dec;34(11-12):758-63. doi: 10.1055/s-2002-38259. Horm Metab Res. 2002. PMID: 12660895
-
Cellular mechanism by which estradiol protects female ovariectomized mice from high-fat diet-induced hepatic and muscle insulin resistance.Endocrinology. 2013 Mar;154(3):1021-8. doi: 10.1210/en.2012-1989. Epub 2013 Jan 30. Endocrinology. 2013. PMID: 23364948 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen withdrawal and replacement differentially target liver and adipose tissues in female mice fed a high-fat high-sucrose diet: impact of a chronic exposure to a low-dose pollutant mixture☆.J Nutr Biochem. 2019 Oct;72:108211. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2019.07.002. Epub 2019 Jul 11. J Nutr Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31473509
-
Estrogen and voluntary exercise attenuate cardiometabolic syndrome and hepatic steatosis in ovariectomized rats fed a high-fat high-fructose diet.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2019 May 1;316(5):E908-E921. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00466.2018. Epub 2019 Feb 26. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2019. PMID: 30807216
-
Tetragonia tetragonioides (Pall.) Kuntze protects estrogen-deficient rats against disturbances of energy and glucose metabolism and decreases proinflammatory cytokines.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017 Mar;242(6):593-605. doi: 10.1177/1535370216683835. Epub 2016 Dec 13. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017. PMID: 28241734 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abildgaard J., et al. Ectopic lipid deposition is associated with insulin resistance in postmenopausal women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018;103(9):3394–3404. - PubMed
-
- Al-Qahtani S.M., et al. 17beta-Estradiol suppresses visceral adipogenesis and activates brown adipose tissue-specific gene expression. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Invest. 2017;29(1):13–26. - PubMed
-
- Babaei P., et al. Effects of ovariectomy and estrogen replacement therapy on visceral adipose tissue and serum adiponectin levels in rats. Menopause Int. 2010;16(3):100–104. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

