Do We Need Anthracyclines for Elderly Patients with Triple-Negative Breast Cancer?
- PMID: 40331126
- PMCID: PMC12052345
- DOI: 10.1159/000544906
Do We Need Anthracyclines for Elderly Patients with Triple-Negative Breast Cancer?
Abstract
Objectives: Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) requires chemotherapy-based systemic treatment which is usually anthracycline-based (AB). The cardiotoxicity of AB regimens is especially relevant in the elderly population. Therefore, we retrospectively compared survival and toxicity between elderly patients with early TNBC receiving AB or anthracycline-free (AF) adjuvant chemotherapy to evaluate whether elderly patients with TNBC could be spared anthracycline-related toxicity without compromising survival.
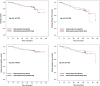
Methods: The study population comprised 221 women with TNBC older than 65 years from the SUCCESS A and SUCCESS C studies, who underwent primary surgery and received either AB (3x fluorouracil-epirubicin-cyclophosphamide followed by 3x docetaxel) or AF (6x docetaxel-cyclophosphamide) adjuvant chemotherapy according to a standardized protocol. The two groups were compared regarding clinicopathological parameters (pT, pN, grading, histological subtype, type of surgery, adjuvant radiotherapy) and side effects using chi-square tests, and regarding survival (overall survival, invasive disease-free survival, breast-cancer specific survival, distant disease-free survival) using log-rank tests and Cox regressions.
Results: There was no significant difference between the two groups regarding any of the clinicopathological parameters, and no significant difference was observed in survival parameters. However, elderly patients with the AB regime had significantly more often grade 3 or 4 adverse events (75.2% vs. 50.6%, p < 0.001) during adjuvant chemotherapy than patients with the AF regimen.
Conclusion: In our retrospective analysis of SUCCESS A and C trial, the use of AF chemotherapy in elderly patients with TNBC was associated with similar survival rates but less toxicity compared to AB chemotherapy. Further randomized controlled trials with AF regimen focusing on elderly patients with TNBC are necessary to confirm our results.
Keywords: Adjuvant chemotherapy; Anthracycline-free; Anthracyclines; Elderly; Side effects; Survival; Triple-negative breast cancer.
© 2025 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
S.L. received honoraria from Lilly, Novartis, Theramex, Gedeon Richter, and Roche; V.F. received honoraria from Novartis and BD; T.F. received honoraria from Novartis and Lilly; F.M. got travel support from Lilly; K.P. obtained honoraria from Gilead, Novartis, and Pfizer, and research grants (constitutional) from AstraZeneca; H.S. got travel support from Daiichi Sankyo and Gilead, and received honoraria from Novartis; D.D. has no conflict of interest to disclose; S.H. received research funding and honoraria from Clovis Oncology, Inc., GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Roche, AstraZeneca, and Pfizer, and participated in advisory boards for Novartis, G.S.K., and Merck Sharp & Dome Corporation; B.R. acquired honoraria and research funding from AstraZeneca and Novartis; W.J. obtained honoraria and/or research funding from AstraZeneca, Cellgene, Chugai Daiichi Sankyo, Aisai, ExactScience, G.S.K., Janssen, Lilly, Menarini, M.S.D., Novartis, Sanofi-Aventis, Roche, Pfizer, Seagen, Gilead, and Inivata Guardant Health; E.L. received travel expenses from Lilly. W.J. was a member of the journal’s Editorial Board at the time of submission.
Figures
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–49. - PubMed
-
- Alberg AJ, Singh S. Epidemiology of breast cancer in older women: implications for future healthcare. Drugs Aging. 2001;18(10):761–72. - PubMed
-
- Diab SG, Elledge RM, Clark GM. Tumor characteristics and clinical outcome of elderly women with breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;92(7):550–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources