Patient and caregiver experiences with hydrocortisone injections in adrenal crisis: a mixed-methods cross-sectional study
- PMID: 40331138
- PMCID: PMC12053486
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1544502
Patient and caregiver experiences with hydrocortisone injections in adrenal crisis: a mixed-methods cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: Adrenal crisis is the leading cause of death in patients with adrenal insufficiency, and prevention requires immediate parenteral hydrocortisone administration. However, most patients do not receive their home emergency hydrocortisone injection. Our study aimed to investigate barriers and enablers to using emergency hydrocortisone injections in managing adrenal crises.
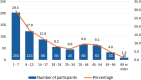
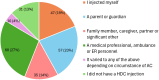
Methods: This mixed-methods observational study utilized an online survey distributed through two U.S.-based patient advocacy groups. A total of 688 respondents completed the survey, including 485 (70%) parents/caregivers of individuals with adrenal insufficiency and 203 (30%) adults with adrenal insufficiency. Qualitative free-text responses were analyzed using thematic content analysis, with subsequent quantification of identified barriers and enablers to administering parenteral hydrocortisone during adrenal crises.
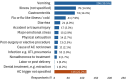
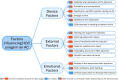
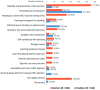
Results: Over 60% of patients with adrenal insufficiency had required parenteral hydrocortisone for an adrenal crisis, yet fewer than 20% managed to self-inject. Thirteen barriers and nine enablers were identified across three thematic domains: device factors, external factors, and emotional factors. Key barriers included the complexity of the multi-step hydrocortisone injection process (81%), injection-related anxiety and lack of confidence (18%), challenges accessing the correct hydrocortisone formulation or equipment (38%), and inadequate support for managing adrenal crises (29%). Key enablers included the effectiveness of hydrocortisone (14%), the convenience of the combined powder-and-diluent hydrocortisone vial (36%), and patient education (4%). Notably, 97% of participants expressed a preference for a hydrocortisone autoinjector to enhance self-injection capabilities.
Conclusion: Effective adrenal crisis management requires comprehensive, evidence-based interventions across patient, healthcare, and societal levels. This should include the development of user-friendly hydrocortisone delivery devices, individualized patient education, healthcare system reforms, and public awareness.
Keywords: adrenal crisis; adrenal insufficiency; congenital adrenal hyperplasia; hydrocortisone injection; parenteral glucocorticoid therapy; self-management.
Copyright © 2025 Llahana, Anthony, Sarafoglou, Geffner and Ross.
Conflict of interest statement
SL has received consulting and invited speaker fees from Recordati, Ipsen, and Neurocrine Pharmaceuticals. JA is Founder and Chief Strategy Officer for SOLUtion Medical which is developing injector products for adrenal crisis treatment. KS serves as a consultant for Neurocrine Biosciences, Spruce Biosciences, Crinetics Pharmaceuticals, Adrenas Therapeutics; Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Novo Nordisk and Eton Pharmaceuticals on behalf of University of Minnesota Medical School, but does not receive personal income for these activities. MG receives consulting fees from Adrenas, Aeterna Zentaris, Ascendis, Eton Pharmaceuticals, Novo Nordisk, Neurocrine Biosciences, Pfizer, Spruce Biosciences, Theratechnologies Inc., and Tolmar; and royalties from McGraw-Hill and UpToDate. RR is a consultant to Neurocrine Biosciences.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Factors influencing self-management of adrenal crisis in patients with adrenal insufficiency: a qualitative study.Endocr Connect. 2025 Apr 28;14(5):e240651. doi: 10.1530/EC-24-0651. Print 2025 May 1. Endocr Connect. 2025. PMID: 40214077 Free PMC article.
-
People With Adrenal Insufficiency Who Are in Adrenal Crisis Are Frequently Unable to Self-Administer Rescue Injections.Endocr Pract. 2025 May;31(5):625-630. doi: 10.1016/j.eprac.2025.02.017. Epub 2025 Mar 3. Endocr Pract. 2025. PMID: 40043845
-
A retrospective analysis of adrenal crisis in steroid-dependent patients: causes, frequency and outcomes.BMC Endocr Disord. 2019 Dec 2;19(1):129. doi: 10.1186/s12902-019-0459-z. BMC Endocr Disord. 2019. PMID: 31791297 Free PMC article.
-
Extensive expertise in endocrinology. Adrenal crisis.Eur J Endocrinol. 2015 Mar;172(3):R115-24. doi: 10.1530/EJE-14-0824. Epub 2014 Oct 6. Eur J Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25288693 Review.
-
Adrenal crises: perspectives and research directions.Endocrine. 2017 Feb;55(2):336-345. doi: 10.1007/s12020-016-1204-2. Epub 2016 Dec 19. Endocrine. 2017. PMID: 27995500 Review.
Cited by
-
Factors influencing self-management of adrenal crisis in patients with adrenal insufficiency: a qualitative study.Endocr Connect. 2025 Apr 28;14(5):e240651. doi: 10.1530/EC-24-0651. Print 2025 May 1. Endocr Connect. 2025. PMID: 40214077 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

