Sodium aescinate promotes apoptosis of pancreatic stellate cells and alleviates pancreatic fibrosis by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/FOXO1 signaling pathways
- PMID: 40331192
- PMCID: PMC12052937
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1554260
Sodium aescinate promotes apoptosis of pancreatic stellate cells and alleviates pancreatic fibrosis by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/FOXO1 signaling pathways
Abstract
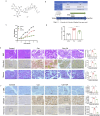
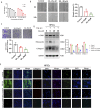
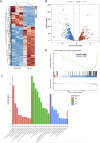
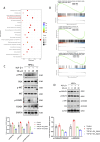
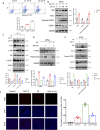
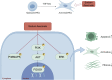
Chronic pancreatitis (CP) is an inflammatory disease of progressive pancreatic fibrosis, and pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs) are key cells involved in pancreatic fibrosis. To date, there are no clinical therapies available to reverse inflammatory damage or pancreatic fibrosis associated with CP. Sodium Aescinate (SA) is a natural mixture of triterpene saponins extracted from the dried and ripe fruits of horse chestnut tree. It has been shown to have anti-inflammatory and anti-edematous effects. This study aims to explore the therapeutic potential of SA in CP and the molecular mechanism of its modulation. Through in vivo animal models and experiments, we found that SA significantly alleviated pancreatic inflammation and fibrosis in caerulein-induced CP mice model. In addition, SA inhibited the proliferation, migration and activation of PSCs as well as promoted apoptosis of PSCs through a series of experiments on cells in vitro including CCK-8 assay, Western blotting, immunofluorescence staining, wound-healing assay, Transwell migration assays, flow cytometric analysis, etc. Further RNA sequencing and in vitro validation assays revealed that inhibition of the PI3K/AKT/FOXO1 signaling pathway was involved in the SA mediated promotion of PSCs apoptosis, thus alleviating pancreatic fibrosis. In conclusion, this study revealed that SA may have promising potential as therapeutic agent for the treatment of CP, and the PI3K/AKT/FOXO1 pathway is a potential therapeutic target for pancreatic inflammation and fibrosis.
Keywords: PI3K/AKT/FOXO1 signaling pathway; apoptosis; chronic pancreatitis (CP); pancreatic fibrosis; pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs); sodium aescinate (SA).
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Xu, Wang, Lin, Zheng, Liu, Li, Jiang, Wang and Zeng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

