Metformin in gynecological disorders: pathogenic insights and therapeutic implications
- PMID: 40331195
- PMCID: PMC12052884
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1526709
Metformin in gynecological disorders: pathogenic insights and therapeutic implications
Abstract
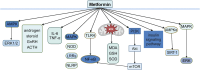
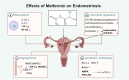
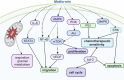
Metformin, the most widely used anti-diabetic drug, has been demonstrated to exert various effects, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, and cardioprotective properties. Due to its affordability and low toxicity profile, metformin is increasingly used to prevent or treat a wide range of gynecological disorders, as evidenced by epidemiological studies, clinical trials, and animal and in vitro studies. Trial findings for non-cancer conditions such as endometriosis, premature ovarian failure (POF), and uterine fibroids remain controversial and insufficient. However, most current clinical trials for polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) and gynecological malignancies are ongoing phase II-III trials. The pharmacological effects of metformin have been shown to target the insulin-like growth factor (IGF), AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT, MAPK, NF-κB, and other signal transduction pathways, highlighting its potential in the treatment of gynecological disorders. In this review, we discuss the biological impacts of metformin and the mechanisms of action pertinent to the treatment of different gynecological disorders.
Keywords: endometriosis; gynecologic malignancies; metformin; ovary; polycystic ovary syndrome; premature ovarian failure; uterus.
Copyright © 2025 Nie, Wang, Mo, Zhou, Zha, Lash and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Metformin use and gynecological cancers: A novel treatment option emerging from drug repositioning.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2016 Sep;105:73-83. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2016.06.006. Epub 2016 Jun 18. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2016. PMID: 27378194 Review.
-
Novel insights into the synergistic effects of selenium nanoparticles and metformin treatment of letrozole - induced polycystic ovarian syndrome: targeting PI3K/Akt signalling pathway, redox status and mitochondrial dysfunction in ovarian tissue.Redox Rep. 2023 Dec;28(1):2160569. doi: 10.1080/13510002.2022.2160569. Redox Rep. 2023. PMID: 36661246 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic effects and molecular mechanisms of quercetin in gynecological disorders.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Apr;173:116418. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116418. Epub 2024 Mar 9. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38461683 Review.
-
Liuwei Dihuang Pills alleviate the polycystic ovary syndrome with improved insulin sensitivity through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Mar 25;250:111965. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.111965. Epub 2019 Jun 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31185267
-
Metformin Ameliorates Uterine Defects in a Rat Model of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.EBioMedicine. 2017 Apr;18:157-170. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.03.023. Epub 2017 Mar 18. EBioMedicine. 2017. PMID: 28336389 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abuelezz N. Z., Shabana M. E., Abdel-Mageed H. M., Rashed L., Morcos G. N. B. (2020). Nanocurcumin alleviates insulin resistance and pancreatic deficits in polycystic ovary syndrome rats: insights on PI3K/AkT/mTOR and TNF-alpha modulations. Life Sci. 256, 118003. 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118003 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alhujaily M., Abbas H., Xue M. Z., de la Fuente A., Rabbani N., Thornalley P. J. (2021). Studies of glyoxalase 1-linked Multidrug resistance reveal Glycolysis-derived reactive metabolite, Methylglyoxal, is a common contributor in cancer chemotherapy targeting the Spliceosome. Front. Oncol. 11, 748698. 10.3389/fonc.2021.748698 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

