Constant pH Molecular Dynamics Simulation of pH Effects on Amyloid-β Structure, Dynamics, and Metal-Binding
- PMID: 40331332
- PMCID: PMC12172581
- DOI: 10.1002/chem.202500547
Constant pH Molecular Dynamics Simulation of pH Effects on Amyloid-β Structure, Dynamics, and Metal-Binding
Abstract
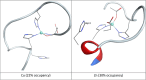
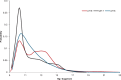
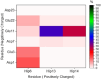
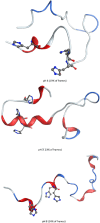
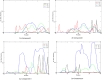
We report the first molecular dynamics simulations to examine the effect of pH on the structure, dynamics, and metal-binding ability of amyloid-β, the peptide implicated in the onset of Alzheimer's disease. We show that in the pH range of 6 to 8 only histidine residues show variable protonation, that predicted pKa values are in agreement with experimental data, and that changes in pH affect the size, flexibility, and secondary structure of the peptide. The binding of Cu(II) or Zn(II) to the peptide induces a shift of 1 to 1.5 pKa units in unbound histidine residues, while metal binding modes associated with higher pH induce significant changes in peptide structure. We speculate on the significance of these findings on results showing pH dependence as well as on Cu(II) and Zn(II) modulation of aggregation of Amyloid-β.
Keywords: amyloid‐β; constant pH; copper; molecular dynamics; secondary structure; zinc.
© 2025 The Author(s). Chemistry – A European Journal published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The binding of kojic acid dimer and its Zn(II) and Cu(II) complexes at the beta-amyloid peptide: A DFT-based computational assessment.J Inorg Biochem. 2025 Oct;271:112979. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2025.112979. Epub 2025 Jun 20. J Inorg Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40570779
-
Oligomeric Protein Complexes Formed by Beta Amyloid Peptides and Their Molecular Associates.Chemistry. 2025 Jul 8;31(38):e202501099. doi: 10.1002/chem.202501099. Epub 2025 Jun 6. Chemistry. 2025. PMID: 40432382
-
Metal binding modes of Alzheimer's amyloid beta-peptide in insoluble aggregates and soluble complexes.Biochemistry. 2000 Jun 13;39(23):7024-31. doi: 10.1021/bi0002479. Biochemistry. 2000. PMID: 10841784
-
Transition Metal Ion Interactions with Disordered Amyloid-β Peptides in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer's Disease: Insights from Computational Chemistry Studies.J Chem Inf Model. 2019 May 28;59(5):1782-1805. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.8b00983. Epub 2019 Apr 15. J Chem Inf Model. 2019. PMID: 30933519 Review.
-
Role of metal ions in the self-assembly of the Alzheimer's amyloid-β peptide.Inorg Chem. 2013 Nov 4;52(21):12193-206. doi: 10.1021/ic4003059. Epub 2013 Apr 22. Inorg Chem. 2013. PMID: 23607830 Review.
References
-
- a) Weibull M. G. M., Simonsen S., Oksbjerg C. R., Tiwari M. K., Hemmingsen L., J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 24, 1197; - PubMed
- b) Atrian‐Blasco E., Conte‐Daban A., Hureau C., Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 12750; - PMC - PubMed
- c) Yi Y., Lim M. H., RSC Chem. Biol. 2023, 4, 121; - PMC - PubMed
- d) Abelein A., Acc. Chem. Res. 2023, 56, 2653. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baptista A. M., Martel P. J., Petersen S. B., Proteins. 1997, 27, 523. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

