SIRT2-mediated ACSS2 K271 deacetylation suppresses lipogenesis under nutrient stress
- PMID: 40331334
- PMCID: PMC12058118
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.97019
SIRT2-mediated ACSS2 K271 deacetylation suppresses lipogenesis under nutrient stress
Abstract
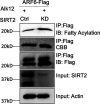
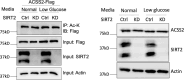
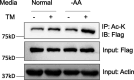
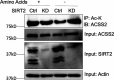
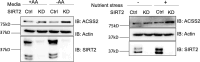
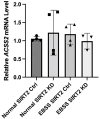
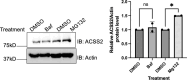
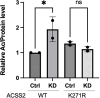
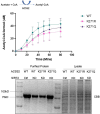
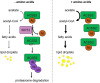
De novo lipogenesis is associated with the development of human diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and obesity. At the core of lipogenesis lies acetyl coenzyme A (CoA), a metabolite that plays a crucial role in fatty acid synthesis. One of the pathways contributing to the production of cytosolic acetyl-CoA is mediated by acetyl-CoA synthetase 2 (ACSS2). Here, we reveal that when cells encounter nutrient stress, particularly a deficiency in amino acids, Sirtuin 2 (SIRT2) catalyzes the deacetylation of ACSS2 at the lysine residue K271. This results in K271 ubiquitination and subsequently proteasomal degradation of ACSS2. Substitution of K271 leads to decreased ubiquitination of ACSS2, increased ACSS2 protein level, and thus increased lipogenesis. Our study uncovers a mechanism that cells employ to efficiently manage lipogenesis during periods of nutrient stress.
Keywords: SIRT2; acetyl-CoA synthetase 2; acetylation; biochemistry; cell biology; chemical biology; human; lipogenesis; mouse; nutrient stress; ubiquitylation.
© 2024, Karim et al.
Conflict of interest statement
RK, WT, CB, HL No competing interests declared
Figures






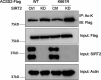
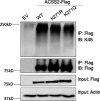
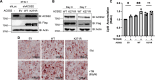
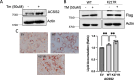
Update of
- doi: 10.1101/2024.02.27.582293
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.97019.1
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.97019.2
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

