Design Principles of Nanosensors for Multiplex Detection of Contaminants in Food
- PMID: 40331479
- PMCID: PMC12232259
- DOI: 10.1002/smll.202412271
Design Principles of Nanosensors for Multiplex Detection of Contaminants in Food
Abstract
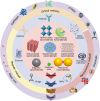
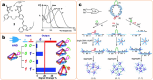
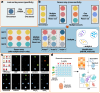
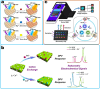
The rapid and cost-effective detection of food contaminants such as toxins and pathogens is a major challenge and a key concern for food safety. To this end, innovative, fast, cost-effective, and easy-to-use sensors must be developed at the point where food is produced, distributed, and consumed. Therefore, timely detection and response to food contaminants can improve human health and reduce economic burden. However, affordable sensor technologies with specificity, sensitivity, and speed are required, which can be used by non-specialized personnel and enable high throughput analysis. In this respect, advances in the development of nanoparticle-based sensors, i.e., nanosensors, have shown the potential to provide the much-anticipated versatile sensors. In addition, multiplex detection, i.e., the ability to detect multiple targets simultaneously, is another strategy facilitated by nanoparticle-based sensors and will enable further improvements in sensor performance that are important for developing effective monitoring. This review summarizes the nanosensors for multiplex sensing of food samples with respect to hazardous contaminates reported over the past few years. In addition, special attention is paid to providing the reader with promising design principles and the current performance of the sensitivity and selectivity of such sensors for practical requirements, thereby inspiring new ideas for developing further advanced systems.
Keywords: food safety; multiplex; multiplex detection; nanosensors; nanotechnology.
© 2025 The Author(s). Small published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures











Similar articles
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is Your Surgical Helmet System Compromising the Sterile Field? A Systematic Review of Contamination Risks and Preventive Measures in Total Joint Arthroplasty.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 Jun 1;483(6):972-990. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003383. Epub 2025 Feb 5. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 39915114
-
Rapid, point-of-care antigen tests for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 22;7(7):CD013705. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013705.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35866452 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic test accuracy and cost-effectiveness of tests for codeletion of chromosomal arms 1p and 19q in people with glioma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Mar 2;3(3):CD013387. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013387.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35233774 Free PMC article.
-
Can a Liquid Biopsy Detect Circulating Tumor DNA With Low-passage Whole-genome Sequencing in Patients With a Sarcoma? A Pilot Evaluation.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 Jan 1;483(1):39-48. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003161. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 38905450
Cited by
-
Advances in Nanotechnology Research in Food Production, Nutrition, and Health.Nutrients. 2025 Jul 26;17(15):2443. doi: 10.3390/nu17152443. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40806027 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization , WHO Estimates of the Global Burden of Foodborne Diseases: Foodborne Disease Burden Epidemiology Reference Group 2007–2015, World Health Organization; 2015.
-
- Dattani S., Spooner F., Ritchie H., Roser M., Cause of death,Our World in Data 2023, https://ourworldindata.org/causes‐of‐death.
-
- van Dijk M., Morley T., Rau M. L., Saghai Y., Nature Food 2021, 2, 494. - PubMed
-
- Malik A. K., Blasco C., Picó Y., J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 4018. - PubMed
-
- Gazzaz S. S., Rasco B. A., Dong F. M., Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1992, 32, 197. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

