Retinoblastoma: Molecular Evaluation of Tumor Samples, Aqueous Humor, and Peripheral Blood Using a Next-Generation Sequence Panel
- PMID: 40332023
- PMCID: PMC12027083
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26083523
Retinoblastoma: Molecular Evaluation of Tumor Samples, Aqueous Humor, and Peripheral Blood Using a Next-Generation Sequence Panel
Abstract
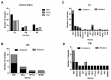
Retinoblastoma was one of the first malignant tumors to be described as a genetic disease and its development occurs from the loss of function of the retinoblastoma gene (RB1). The difficulty in accessing the tumor during diagnosis highlights the need for non-invasive diagnostic methods. Studies have shown that liquid biopsy, obtained from any fluid material in the body, for example blood, contains free tumor cells and free and circulating DNA or RNA, making it a convenient tool for diagnosis and prognosis during cancer treatment without the need for invasive procedures. Taking advantage of these events, given this situation, we investigated molecular alterations in samples from retinoblastoma cases, using the NGS strategy as a powerful tool for characterization and aid in diagnosis and prognosis. Genomic data from 76 patients diagnosed with retinoblastoma, comprising 162 samples, tumor (TU), aqueous humor (AH), and peripheral blood (PB), were analyzed using the Oncomine Childhood Cancer Research Panel (OCCRA®). A total of 22 altered genes were detected, and 54 variants. Of the 76 cases, 29 included paired tumor (TU), aqueous humor (AH), and peripheral blood (PB) samples from the same patient. Alterations in the RB1 gene were detected in 16 of these 29 cases, with concordant alterations identified across all three sample types in three patients. In 12 out of 29 patients, the same genetic alteration was found in both TU and AH. In conclusion, the OCCRA panel enabled the detection, in different samples, of molecular alterations in the RB1 gene, as well as CNAs in the MYCN, ABL2, and MDM4 genes. Limitations of AH were observed, primarily due to the small volume of material available and the consequently low concentration of cell-free DNA (cfDNA). However, as AH provides a viable alternative for analyzing tumors, inaccessible to traditional biopsy methods, liquid biopsy holds significant potential to improve diagnostic accuracy and guide treatment strategies in retinoblastoma cases.
Keywords: aqueous humor; liquid biopsy; next-generation sequence panel; retinoblastoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Simultaneous identification of clinically relevant RB1 mutations and copy number alterations in aqueous humor of retinoblastoma eyes.Ophthalmic Genet. 2020 Dec;41(6):526-532. doi: 10.1080/13816810.2020.1799417. Epub 2020 Aug 17. Ophthalmic Genet. 2020. PMID: 32799607 Free PMC article.
-
Aqueous Humor Liquid Biopsy as a Companion Diagnostic for Retinoblastoma: Implications for Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Therapeutic Options: Five Years of Progress.Am J Ophthalmol. 2024 Jul;263:188-205. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2023.11.020. Epub 2023 Nov 30. Am J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38040321 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor DNA sampling from aqueous humor in retinoblastoma - A report from South Asia.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2024 Jul 1;72(7):1012-1016. doi: 10.4103/IJO.IJO_234_23. Epub 2024 Mar 8. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38454873 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid biopsy in Retinoblastoma: A review.Semin Ophthalmol. 2022 Oct-Nov;37(7-8):813-819. doi: 10.1080/08820538.2022.2078165. Epub 2022 May 23. Semin Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35604935 Review.
-
The Potential of Aqueous Humor Sampling in Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Treatment of Retinoblastoma.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024 Jan 2;65(1):18. doi: 10.1167/iovs.65.1.18. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024. PMID: 38180770 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Global research landscape of retinoblastoma biomarkers: a multidisciplinary bibliometric analysis based on multiple databases (2005-2025).J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2025 Aug 15;151(8):231. doi: 10.1007/s00432-025-06279-7. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40817296 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous