The Yeast Gsk-3 Kinase Mck1 Is Necessary for Cell Wall Remodeling in Glucose-Starved and Cell Wall-Stressed Cells
- PMID: 40332024
- PMCID: PMC12027387
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26083534
The Yeast Gsk-3 Kinase Mck1 Is Necessary for Cell Wall Remodeling in Glucose-Starved and Cell Wall-Stressed Cells
Abstract
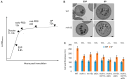
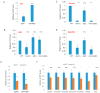
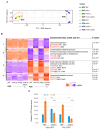
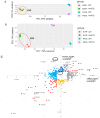
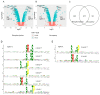
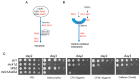
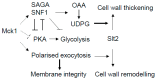
The cell wall integrity (CWI) pathway is responsible for transcriptional regulation of cell wall remodeling in response to cell wall stress. How cell wall remodeling mediated by the CWI pathway is effected by inputs from other signaling pathways is not well understood. Here, we demonstrate that the Mck1 kinase cooperates with Slt2, the MAP kinase of the CWI pathway, to promote cell wall thickening in glucose-starved cells. Integrative analyses of the transcriptome, proteome and metabolic profiling indicate that Mck1 is required for the accumulation of UDP-glucose (UDPG), the substrate for β-glucan synthesis, through the activation of two regulons: the Msn2/4-dependent stress response and the Cat8-/Adr1-mediated metabolic reprogram dependent on the SNF1 complex. Analysis of the phosphoproteome suggests that similar to mammalian Gsk-3 kinases, Mck1 is involved in the regulation of cytoskeleton-dependent cellular processes, metabolism, signaling and transcription. Specifically, Mck1 may be implicated in the Snf1-dependent metabolic reprogram through PKA inhibition and SAGA (Spt-Ada-Gcn5 acetyltransferase)-mediated transcription activation, a hypothesis further underscored by the significant overlap between the Mck1- and Gcn5-activated transcriptomes. Phenotypic analysis also supports the roles of Mck1 in actin cytoskeleton-mediated exocytosis to ensure plasma membrane homeostasis and cell wall remodeling in cell wall-stressed cells. Together, these findings not only reveal the novel functions of Mck1 in metabolic reprogramming and polarized growth but also provide valuable omics resources for future studies to uncover the underlying mechanisms of Mck1 and other Gsk-3 kinases in cell growth and stress response.
Keywords: Mck1; PKA; SAGA; SNF1; Slt2; metabolic reprogramming; polarized growth.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Houjiang Zhou is currently employed by Zhejiang Hisun Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chronological Lifespan in Yeast Is Dependent on the Accumulation of Storage Carbohydrates Mediated by Yak1, Mck1 and Rim15 Kinases.PLoS Genet. 2016 Dec 6;12(12):e1006458. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006458. eCollection 2016 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27923067 Free PMC article.
-
The high osmotic response and cell wall integrity pathways cooperate to regulate transcriptional responses to zymolyase-induced cell wall stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Biol Chem. 2009 Apr 17;284(16):10901-11. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M808693200. Epub 2009 Feb 20. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19234305 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperation between SAGA and SWI/SNF complexes is required for efficient transcriptional responses regulated by the yeast MAPK Slt2.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Sep 6;44(15):7159-72. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw324. Epub 2016 Apr 25. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27112564 Free PMC article.
-
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae GSK-3 beta homologs.Curr Drug Targets. 2006 Nov;7(11):1455-65. doi: 10.2174/1389450110607011455. Curr Drug Targets. 2006. PMID: 17100585 Review.
-
Control of Gene Expression via the Yeast CWI Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 4;23(3):1791. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031791. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163713 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

