Advances in Metabolomics: A Comprehensive Review of Type 2 Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease Interactions
- PMID: 40332079
- PMCID: PMC12027308
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26083572
Advances in Metabolomics: A Comprehensive Review of Type 2 Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease Interactions
Abstract
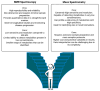
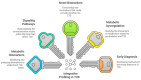
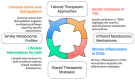
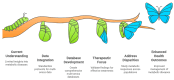
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) and cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are major public health challenges worldwide. Metabolomics, the exhaustive assessment of metabolites in biological systems, offers important insights regarding the metabolic disturbances related to these disorders. Recent advances toward the integration of metabolomics into clinical practice to facilitate the discovery of novel biomarkers that can improve the diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of T2D and CVDs are discussed in this review. Metabolomics offers the potential to characterize the key metabolic alterations associated with disease pathophysiology and treatment. T2D is a heterogeneous disease that develops through diverse pathophysiological processes and molecular mechanisms; therefore, the disease-causing pathways of T2D are not completely understood. Recent studies have identified several robust clusters of T2D variants representing biologically meaningful, distinct pathways, such as the beta cell and proinsulin cluster related to pancreatic insulin secretion, obesity, lipodystrophy, the liver/lipid cluster, glycemia, and blood pressure, and metabolic syndrome clusters representing different pathways causing insulin resistance. Regarding CVDs, recent studies have allowed the metabolomic profile to delineate pathways that contribute to atherosclerosis and heart failure, as well as to the development of targeted therapy. This review also covers the role of metabolomics in integrated metabolic genomics and other omics platforms to better understand disease mechanisms, along with the transition toward precision medicine. This review further investigates the use of metabolomics in multi-metabolite modeling to enhance risk prediction models for predicting the first occurrence of major adverse cardiovascular events among individuals with T2D, highlighting the value of such approaches in optimizing the preventive and therapeutic models used in clinical practice.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; coronary artery disease; metabolites; metabolomics; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Urgent Action Needed as Global Diabetes Cases Increase Four-Fold Over Past Decades. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2025.
-
- Yin X., Bose D., Kwon A., Hanks S.C., Jackson A.U., Stringham H.M., Welch R., Oravilahti A., Silva L.F., Locke A.E., et al. Integrating transcriptomics, metabolomics, and GWAS helps reveal molecular mechanisms for metabolite levels and disease risk. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2022;109:1727–1741. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2022.08.007. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

