Piceatannol Inhibits the Immunostimulatory Functions of Dendritic Cells and Alleviates Experimental Arthritis
- PMID: 40332204
- PMCID: PMC12026827
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26083626
Piceatannol Inhibits the Immunostimulatory Functions of Dendritic Cells and Alleviates Experimental Arthritis
Abstract
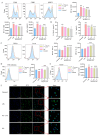
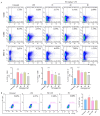
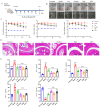
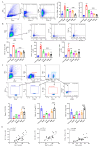
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a highly prevalent systemic autoimmune disease. Recently, natural small molecules have been explored as alternative therapeutic agents. Iris halophila Pall is the traditional herbal medicine, and it is rich in active ingredients with anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects. In our previous study, LC-MS analysis revealed that piceatannol (PIC) is one of the primary active ingredients in the root of Iris tectorum. The purpose of this study was to explore the immunomodulatory effects of PIC on the maturation and function of dendritic cells, as well as on experimental arthritis induced by complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) and incomplete Freund's adjuvant (IFA). Additionally, we aimed to probe into the potential mechanisms underlying the effects of PIC. We first verified the immunosuppressive effect of PIC using flow cytometry and an ELISA. The immunosuppressive mechanism of PIC on dendritic cells (DCs) was investigated through a joint analysis of network pharmacology and Western blotting. Our findings revealed that under Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory conditions, PIC could restrain the maturation and function of DCs (p < 0.001) and decrease the secretion of inflammatory cytokines (p < 0.001) compared to the LPS group. Furthermore, PIC suppressed the activation and polarization of CD4+ T cells, resulting in a decreased proportion of Th1 and Th17 cells (p < 0.001), ultimately improving the symptoms of CFA-induced arthritis in comparison to the model group. The PIC-induced shift in the T helper cell differentiation correlated with the secretion of polarizing cytokines from DCs in the AIA model. Mechanistically, PIC exerted its immunosuppressive function mainly by down-regulating the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) and Nuclear Factor kappa-B (NF-κB) signaling pathways. Collectively, these data unveil the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of a traditional medicine via the inhibition of the immune activation function of DCs in vivo and open up a therapeutic approach for autoinflammatory diseases.
Keywords: dendritic cells; piceatannol; rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

