Genome-Wide Identification and Transcriptome Analysis of P450 Superfamily Genes in Flax (Linum usitatissimum L.)
- PMID: 40332225
- PMCID: PMC12027707
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26083637
Genome-Wide Identification and Transcriptome Analysis of P450 Superfamily Genes in Flax (Linum usitatissimum L.)
Abstract
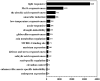
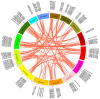
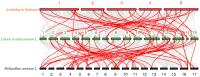
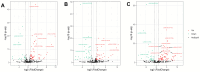
Flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) seed is rich in α-linolenic acid, lignans, and fiber, which have potential health benefits. However, the potential toxicity of its cyanogenic glycosides limits its widespread use. The cytochrome P450 gene family is one of the largest gene families in plants and is involved in synthesizing phytohormones, secondary metabolites, and various defense compounds. Two P450 genes have been found to be important enzymes for the biosynthesis of cyanogenic glycosides in common sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench). However, the P450 gene family and its involvement in cyanogenic glycoside synthesis have been less studied in flax. In previous studies, we assembled a high-quality flax genome. In this study, a total of 412 P450 genes were identified in the flax genome, with molecular weights in the range of 7.42 kDa to 154.5 kDa and encoding amino acid lengths between 67 and 1378. These genes belonged to 48 families under eight clans and were distributed across 15 chromosomes. The number of introns varied from 0 to 14. Thirty-nine cis-acting elements were identified within 1500 bp upstream of the promoter, mainly related to the light response. There were 147 segmental duplications and 53 tandem duplication events among these P450 genes. Eleven genes potentially related to cyanogenic glycoside synthesis were identified by transcriptome analysis, and the RT-qPCR results verified the reliability of the transcriptome analysis. This study lays the foundation for the classification and functional study of the flax P450 gene family. The results will be useful for breeding new low-cyanogenic-glycoside flax varieties by genetic engineering.
Keywords: RNA-seq; cyanogenic glycosides; cytochrome; flax genome; gene family.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Genome-wide identification and expression pattern analysis of the cinnamoyl-CoA reductase gene family in flax (Linum usitatissimum L.).BMC Genomics. 2025 Mar 31;26(1):315. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11481-5. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40165056 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profiling of Dehydration-Responsive Element-Binding Family Genes in Flax (Linum usitatissimum L.).Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 27;26(7):3074. doi: 10.3390/ijms26073074. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40243796 Free PMC article.
-
A genome-wide analysis of the flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) dirigent protein family: from gene identification and evolution to differential regulation.Plant Mol Biol. 2018 May;97(1-2):73-101. doi: 10.1007/s11103-018-0725-x. Epub 2018 Apr 30. Plant Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29713868
-
Phylogenomic analysis of UDP glycosyltransferase 1 multigene family in Linum usitatissimum identified genes with varied expression patterns.BMC Genomics. 2012 May 8;13:175. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-175. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22568875 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification of ATP binding cassette (ABC) transporter and heavy metal associated (HMA) gene families in flax (Linum usitatissimum L.).BMC Genomics. 2020 Oct 19;21(1):722. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-07121-9. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 33076828 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wu C.F., Xu X.M., Huang S.H., Deng M.C., Feng A.J., Peng J., Yuan J.P., Wang J.H. An efficient fermentation method for the degradation of cyanogenic glycosides in flaxseed. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2012;29:1085–1091. doi: 10.1080/19440049.2012.680202. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Oomah B.D., Mazza G., Kenaschuk E.O. Cyanogenic compounds in flaxseed. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1992;40:1346–1348. doi: 10.1021/jf00020a010. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BR231513/the Basic Research Operating Expenses Program for Colleges and Universities directly under the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region
- 32160448/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2023MS03008/the Inner the Mongolia Natural Science Foundationx
- 2024MS03026/the Inner the Mongolia Natural Science Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

