Reduction in Gonad Development and Sperm Motility in Male Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens via RNAi-Mediated Knockdown of tramtrack
- PMID: 40332247
- PMCID: PMC12026634
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26083643
Reduction in Gonad Development and Sperm Motility in Male Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens via RNAi-Mediated Knockdown of tramtrack
Abstract
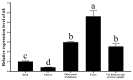
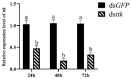
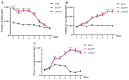
The brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens, a major rice pest, threatens global food security through rapid reproduction. This study investigates the role of the tramtrack (ttk) gene in male reproductive development and spermatogenesis using RNA interference (RNAi). Gene expression analysis revealed higher ttk levels in testes. RNAi-mediated knockdown of ttk in fourth-instar male nymphs reduced its expression by up to 80%, leading to severely impaired gonad development. Testes, vas deferens, and accessory glands in treated males exhibited 8-89% volume reductions compared to controls, accompanied by a 51-69% decline in sperm count and 60-85% reduction in sperm motility. Consequently, eggs fertilized by treated males showed a 73% decrease in hatching rates, with arrested embryonic development. These findings demonstrate ttk's critical role in spermatogenesis and gonad maturation in N. lugens, highlighting its potential as an RNAi target for sustainable pest control strategies.
Keywords: Nilaparvata lugens; RNAi; gonad maturation; spermatogenesis; tramtrack.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of ttk on development and courtship of male Nilaparvata lugens.Pest Manag Sci. 2024 Dec;80(12):6465-6472. doi: 10.1002/ps.8381. Epub 2024 Aug 22. Pest Manag Sci. 2024. PMID: 39172052
-
Effect of RNAi-mediated knockdown of NlTOR gene on fertility of male Nilaparvata lugens.J Insect Physiol. 2017 Apr;98:149-159. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2017.01.002. Epub 2017 Jan 7. J Insect Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28069465
-
Male-specific lethal-3 gene is critical for survival and fecundity in rice brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2024 Dec;175:104207. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2024.104207. Epub 2024 Oct 26. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39490907
-
Troponin C is required for copulation and ovulation in Nilaparvata lugens.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2025 Feb;177:104258. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2025.104258. Epub 2025 Jan 14. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39818321
-
RNAi-mediated knockdown of papilin gene affects the egg hatching in Nilaparvata lugens.Pest Manag Sci. 2024 Sep;80(9):4779-4789. doi: 10.1002/ps.8194. Epub 2024 Jun 4. Pest Manag Sci. 2024. PMID: 38837578
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

