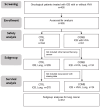
Combined Immune Checkpoint Blockade and Helixor® Therapy in Oncology: Real-World Tolerability and Subgroup Survival (ESMO GROW)
- PMID: 40332249
- PMCID: PMC12027740
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26083669
Combined Immune Checkpoint Blockade and Helixor® Therapy in Oncology: Real-World Tolerability and Subgroup Survival (ESMO GROW)
Abstract
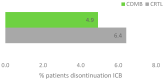
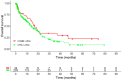
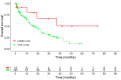
Real-world data (RWD) play a crucial role in identifying key subgroups and assessing multimodal oncology therapies, including integrative and palliative care. Immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) has improved survival, and its combination with complementary therapies like Viscum album L. extracts (VA) may enhance outcomes. This RWD study, based on the Network Oncology registry and ESMO-GROW guidelines, analyzed oncological patients receiving PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors alone or with Helixor® VA (HVA) extracts. Primary and secondary objectives were tolerability and overall survival. Statistical analyses included Kaplan-Meier survival curves and Cox regression. Among 405 cancer patients, 344 received ICB alone (CTRL) and 61 received ICB + HVA (COMB). Lung cancer was predominant (78.6%). Adverse event-related discontinuation was lower in COMB (4.9% vs. 6.4%, p = 0.25). In non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients, the 3-year survival rate was significantly higher in COMB (34.3% vs. 17.2%, p = 0.02). In female NSCLC patients, COMB was significantly associated with a reduced death risk of 91.2% (aHR: 0.088; 95% CI: 0.009-0.783). Our RWD findings show the favorable tolerability of combinatorial ICB + HVA in several tumor entities and underscore its potential to improve survival in NSCLC particularly in female NSCLC patients, warranting further investigation.
Keywords: Helixor® Viscum album therapy; PD-1 inhibitor; PD-L1 inhibitor; lung cancer; non-small cell lung cancer; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
F.S. reports receiving grants from Abnoba GmbH, Helixor Heilmittel GmbH, and Astrazeneca GmbH, outside the submitted work. P.G. reports travel expenses from Ipsen Pharma and research grants from Helixor Heilmittel GmbH, outside the submitted work. H.W. reports honoraria from AstraZeneca and Berlin-Chemie, outside the submitted work. C.G. reports honoraria from AstraZeneca, Novartis, Chiesi, the German Society of Pneumology, Takeda, the German S3-Guideline on Complementary Medicine in the Treatment of Oncological Patients, and the Brandenburgian Cancer Society, all outside the submitted work. C.G. has also received grants from Wala AG and Iscador AG, outside the submitted work. C.G. is a member of the European Respiratory Society, the German Society of Pneumology, Health Care Without Harm, the German Alliance for Climate Change and Health, and the Society of Anthroposophic Physicians. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Huang A., Wang K., Penn Medicine . Combo Immunotherapy Makes Waves of Cancer-Fighting T Cells. Penn Medicine; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2024. [(accessed on 9 April 2025)]. Available online: https://www.pennmedicine.org/news/news-releases/2024.
-
- Schad F., Thronicke A., Hofheinz R.D., Klein R., Grabowski P., Oei S.L., Wüstefeld H., Grah C. Immune Checkpoint Blockade Combined with AbnobaViscum® Therapy Is Linked to Improved Survival in Advanced or Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients: A Registry Study in Accordance with the ESMO Guidance for Reporting Real-World Evidence. Pharmaceuticals. 2024;17:1713. doi: 10.3390/ph17121713. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

