Natriuretic Peptides and Soluble ST2 Improve Echocardiographic and Invasive Long-Term Survival Prediction in Patients Evaluated for Diastolic Dysfunction
- PMID: 40332321
- PMCID: PMC12027908
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26083713
Natriuretic Peptides and Soluble ST2 Improve Echocardiographic and Invasive Long-Term Survival Prediction in Patients Evaluated for Diastolic Dysfunction
Abstract
This study aimed to investigate the impact of long-term survival on cardiac serum biomarkers such as natriuretic peptides (mid-regional pro-atrial natriuretic peptide [MR-proANP], B-type natriuretic peptide [BNP], N-terminal prohormone BNP [NT-proBNP]), soluble ST2 (sST2), galectin-3 and mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin (MR-proAMD). Consecutive patients hospitalized in a tertiary center, undergoing echocardiographic and invasive left cardiac catheterization for diastolic dysfunction assessment were prospectively included in this study. Cardiac biomarkers were determined from pre-procedural peripheral venous blood samples. A total of 110 patients were included, with a median follow-up of 1.66 (1.23-2.16) years during which 16 (14.5%) patients died. A total of 45.4% (50) of patients had diastolic dysfunction. In the univariate Cox regression, long-term survival was predicted by BNP (p < 0.0001, HR = 0.39 [0.20-0.53]), NT-proBNP (p < 0.0001, HR = 0.40 [0.22-0.55]), MR-proANP (p = 0.001, HR = 0.30 [0.11-0.46]), sST2 (p < 0.0001, HR = 0.47 [0.30-0.60]), but not with MR-proAMD (p = 0.77) or galectin-3 (p = 0.76). In the final stepwise multivariable Cox regression non-invasive and invasive models, NT-proBNP and sST2 remained independent predictors of survival. Natriuretic peptides (BNP and NT-proBNP) and sST2 were predictors of long-term survival, while MR-proANP, MR-proADM and galectin-3 did not have predictive values. NT-proBNP and sST2 improved survival prediction in both a non-invasive scenario (including clinical, serum and echocardiographic parameters) and an invasive clinical scenario (including left heart catheterization parameters). The sST2 pathway could provide a target for therapeutic intervention.
Keywords: B-type natriuretic peptide; N-terminal prohormone B-type natriuretic peptide; galectin-3; mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin; mid-regional pro-atrial natriuretic peptide; soluble ST2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
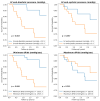

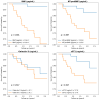

Similar articles
-
Natriuretic peptides and soluble ST2 improves echocardiographic diagnosis of elevated left ventricular filling pressures.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 27;14(1):22171. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-73349-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39333652 Free PMC article.
-
Mid-regional pro-atrial natriuretic peptide and pro-adrenomedullin testing for the diagnostic and prognostic evaluation of patients with acute dyspnoea.Eur Heart J. 2012 Sep;33(17):2197-205. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehs136. Epub 2012 May 29. Eur Heart J. 2012. PMID: 22645194 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic performance and reference values of novel biomarkers of paediatric heart failure.Heart. 2016 Oct 15;102(20):1633-9. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2016-309460. Epub 2016 May 24. Heart. 2016. PMID: 27220692
-
Biomarkers and diagnostics in heart failure.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Dec;1832(12):2442-50. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2012.12.014. Epub 2013 Jan 9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23313577 Review.
-
Biomarkers and heart disease.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014 Oct;18(19):2927-35. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25339488 Review.
References
-
- McDonagh T.A., Metra M., Adamo M., Gardner R.S., Baumbach A., Böhm M., Burri H., Butler J., Čelutkienė J., Chioncel O., et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: Developed by the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) With the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2021;42:3599–3726. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab368. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Oremus M., McKelvie R., Don-Wauchope A., Santaguida P.L., Ali U., Balion C., Hill S., Booth R., Brown J.A., Bustamam A., et al. A systematic review of BNP and NT-proBNP in the management of heart failure: Overview and methods. Heart Fail. Rev. 2014;19:413–419. doi: 10.1007/s10741-014-9440-0. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

