Acanthopanax Senticosus Saponins Prevent Cognitive Decline in Rats with Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 40332373
- PMCID: PMC12027677
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26083715
Acanthopanax Senticosus Saponins Prevent Cognitive Decline in Rats with Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
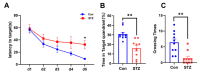
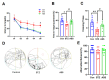
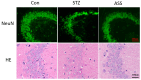
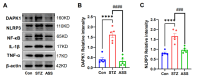
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive degenerative disease of the nervous system that affects older adults. Its main clinical manifestations include memory loss, cognitive dysfunction, abnormal behaviour, and social dysfunction. Neuroinflammation is typical in most neurodegenerative diseases, such as AD. Therefore, suppressing inflammation may improve AD symptoms. This study investigated the neuroprotective effects of Acanthopanax senticosus saponins (ASS) in an AD model induced by streptozotocin (STZ). Here, we characterised a rat model of STZ-induced AD with the parallel deterioration of memory loss and neuroinflammation. Following the end of the treatment with ASS (50 mg/kg for 14 consecutive days), behavioural tests (Morris water maze test, Y-maze test) were performed on the rat, and the molecular parameters (DAPK1, Tau5, p-Tau, NF-κB, IL-1β, TNF-α, and NLRP3) of the rat hippocampus were also assessed. We demonstrated that ASS, which has potent anti-inflammatory effects, can reduce neuroinflammation and prevent cognitive impairment. In the water maze test, ASS-treated groups exhibited significantly increased average escape latency (p < 0.05), the percentage of stay in the target quadrant (p < 0.05), and the number of times each group of rats crossed the platform (p < 0.05) compared to the negative control. And ASS could reduce the phosphorylation of the Tau protein (p < 0.001) and death-associated protein kinase 1 (DAPK1, p < 0.001) in the hippocampal tissue, improving cognitive impairment in STZ-treated rats by suppressing the inflammatory response; the molecular analysis showed a significant reduction in pro-inflammatory markers like NLRP3, IL-1β, TNF-α, and NF-κB (p < 0.001). It was also discovered that the NF-κB inhibitor SN50 had the same effect. Therefore, the present study used ASS through its anti-inflammatory effects to prevent and treat AD. This study highlights the potential efficacy of ASS in alleviating cognitive dysfunction in AD.
Keywords: Acanthopanax senticosus saponins; Alzheimer’s disease; Tau protein; cognitive decline; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

