TMEM16A Maintains Acrosomal Integrity Through ERK1/2, RhoA, and Actin Cytoskeleton During Capacitation
- PMID: 40332387
- PMCID: PMC12027809
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26083750
TMEM16A Maintains Acrosomal Integrity Through ERK1/2, RhoA, and Actin Cytoskeleton During Capacitation
Abstract
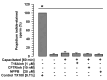
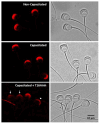
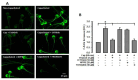
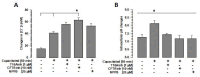
Mammalian spermatozoa undergo a series of physiological and biochemical changes in the oviduct that lead them to acquire the ability to fertilize eggs. During their transit in the oviduct, spermatozoa face a series of environmental changes that can affect sperm viability. A series of ion channels and transporters, as well as the sperm cytoskeleton, allow spermatozoa to remain viable and functional. Cl- channels such as TMEM16A (calcium-activated chloride channel), CFTR (cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator), and ClC3 (chloride voltage-gated channel 3) are some of the ion transporters involved in maintaining cellular homeostasis. They are expressed in mammalian spermatozoa and are associated with capacitation, acrosomal reaction, and motility. However, little is known about their role in maintaining sperm volume. Therefore, this study aimed to determine the mechanism through which TMEM16A maintains sperm volume during capacitation. The effects of TMEM16A were compared to those of CFTR and ClC3. Spermatozoa were capacitated in the presence of specific TMEM16A, CFTR, and ClC3 inhibitors, and the results showed that only TMEM16A inhibition increased acrosomal volume, leading to changes within the acrosome. Similarly, only TMEM16A inhibition prevented actin polymerization during capacitation. Further analysis showed that TMEM16A inhibition also prevented ERK1/2 and RhoA activation. On the other hand, TMEM16A and CFTR inhibition affected both capacitation and spontaneous acrosomal reaction, whereas ClC3 inhibition only affected the spontaneous acrosomal reaction. In conclusion, during capacitation, TMEM16A activity regulates acrosomal structure through actin polymerization and by regulating ERK1/2 and RhoA activities.
Keywords: acrosome structure; bicarbonate influx; chloride channels; fertilization; sperm.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

