The Protective Effect of Topical PACAP38 in Retinal Morphology and Function of Type 2 Diabetic Retinopathy
- PMID: 40332399
- PMCID: PMC12027713
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26083753
The Protective Effect of Topical PACAP38 in Retinal Morphology and Function of Type 2 Diabetic Retinopathy
Abstract
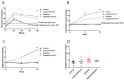
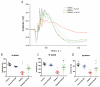
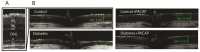
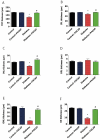
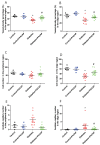
The continuously growing diabetes population is a significant concern with type 2 diabetic retinal disease (T2DRD), which is a leading cause of permanent blindness. However, the underlying pathophysiological mechanism of T2DRD has not yet been fully understood. Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) was first isolated from the ovine hypothalamus based on its stimulating effect on the adenylate cyclase enzyme in anterior pituitary cells. PACAP38 (PACAP with 38 amino acids) activates anti-apoptotic pathways, inhibits pro-apoptotic signaling, and creates an anti-inflammatory environment in the retina. The aim of the present study was to test the possible retinoprotective effect of the topical administration of PACAP38 in a type 2 diabetic animal model induced by a high-fat diet and the intraperitoneally injected low-dose streptozotocin (STZ). Wistar rats were divided into four groups: the control, control + PACAP38, diabetes, and diabetes + PACAP38 groups randomly. Type 2 diabetes was induced with the combination of STZ (30 mg/kg) and a high-fat diet. All rats were treated topically two times a day for 16 weeks: the control + PACAP38 and diabetes + PACAP38 groups were applied with PACAP38 eye drops (1 µg/drop), while the control and diabetes groups were administered using vehicles (artificial tears). The diabetes model was validated by a fasting oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) and C-peptide ELISA test. Animals were monitored during the whole experiment for the progression of the disease using electroretinography (ERG) and optical coherence tomography (OCT). Post-mortem immunohistochemistry and a vessel analysis were performed in the retina samples after 16 weeks. An OGTT, a C-peptide ELISA test, and the investigation of blood parameters proved the development of type 2 diabetes. Significant differences could be detected in visual function between the two diabetic groups at week 16 (in the a-wave, b-wave, and OP amplitudes), where the diabetes PACAP38-treated group was similar to the control ones. OCT measurements correlated with ERG data, where the total retinal thickness was preserved in the diabetes + PACAP38 group. PACAP38 also protected the microvascular structure in the retina. Topically administered PACAP38 has potent neuroprotective effects against type 2 diabetic retinal disease; therefore, it could be a promising therapeutic approach for the treatment of T2DRD.
Keywords: ERG; OCT; PACAP; eye drops; type 2 diabetic retinal disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Atlas I.D. Global diabetes data report 2000–2045. 2023. [(accessed on 9 September 2024)]. Available online: https://diabetesatlas.org/data/en/world/
-
- Sohn E.H., Van Dijk H.W., Jiao C., Kok P.H.B., Jeong W., Demirkaya N., Garmager A., Wit F., Kucukevcilioglu M., van Velthoven M.E.J., et al. Retinal neurodegeneration may precede microvascular changes characteristic of diabetic retinopathy in diabetes mellitus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2016;113:E2655–E2664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1522014113. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

