Long-Read Whole-Genome Sequencing as a Tool for Variant Detection in Inherited Retinal Dystrophies
- PMID: 40332496
- PMCID: PMC12027592
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26083825
Long-Read Whole-Genome Sequencing as a Tool for Variant Detection in Inherited Retinal Dystrophies
Abstract
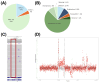
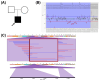
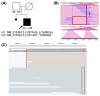
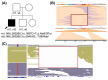
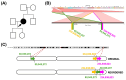
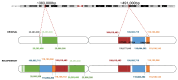
Advances in whole-genome sequencing (WGS) have significantly enhanced our ability to detect genomic variants underlying inherited diseases. In this study, we performed long-read WGS on 24 patients with inherited retinal dystrophies (IRDs) to validate the utility of nanopore sequencing in detecting genomic variations. We confirmed the presence of all previously detected variants and demonstrated that this approach allows for the precise refinement of structural variants (SVs). Furthermore, we could perform genotype phasing by sequencing only the probands, confirming that the variants were inherited in trans. Moreover, nanopore sequencing enables the detection of complex variants, such as transposon insertions and structural rearrangements. This comprehensive assessment illustrates the power of long-read sequencing in capturing diverse forms of genomic variation and in improving diagnostic accuracy in IRDs.
Keywords: inherited retinal dystrophies; long-read sequencing; nanopore sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Arteche-López A., Ávila-Fernández A., Romero R., Riveiro-Álvarez R., López-Martínez M.A., Giménez-Pardo A., Vélez-Monsalve C., Gallego-Merlo J., García-Vara I., Almoguera B., et al. Sanger Sequencing Is No Longer Always Necessary Based on a Single-Center Validation of 1109 NGS Variants in 825 Clinical Exomes. Sci. Rep. 2021;11:5697. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85182-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Perea-Romero I., Gordo G., Iancu I.F., Del Pozo-Valero M., Almoguera B., Blanco-Kelly F., Carreño E., Jimenez-Rolando B., Lopez-Rodriguez R., Lorda-Sanchez I., et al. Genetic Landscape of 6089 Inherited Retinal Dystrophies Affected Cases in Spain and Their Therapeutic and Extended Epidemiological Implications. Sci. Rep. 2021;11:1526. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-81093-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gonzàlez-Duarte R., De Castro-Miró M., Tuson M., Ramírez-Castañeda V., Gils R.V., Marfany G. Scaling New Heights in the Genetic Diagnosis of Inherited Retinal Dystrophies. In: Bowes Rickman C., Grimm C., Anderson R.E., Ash J.D., LaVail M.M., Hollyfield J.G., editors. Retinal Degenerative Diseases. Volume 1185. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Germany: 2019. pp. 215–219. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology.
-
- Reurink J., Weisschuh N., Garanto A., Dockery A., Van Den Born L.I., Fajardy I., Haer-Wigman L., Kohl S., Wissinger B., Farrar G.J., et al. Whole Genome Sequencing for USH2A-Associated Disease Reveals Several Pathogenic Deep-Intronic Variants That Are Amenable to Splice Correction. Hum. Genet. Genom. Adv. 2023;4:100181. doi: 10.1016/j.xhgg.2023.100181. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 824110/European Advanced Infrastructure for Innovative Genomics (EASI-Genomics) project
- PI19/00321- PI20/00851- PI22/00321 and PI22/00579/Instituto de Salud Carlos III (ISCIII) of the Spanish Ministry of Health
- 06/07/0036/Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red en Enfermedades Raras
- PT23/00114/IIS-FJD BioBank
- Fundación Conchita Rábago
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

