Targeting the Ischemic Core: A Therapeutic Microdialytic Approach to Prevent Neuronal Death and Restore Functional Behaviors
- PMID: 40332503
- PMCID: PMC12027531
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26083821
Targeting the Ischemic Core: A Therapeutic Microdialytic Approach to Prevent Neuronal Death and Restore Functional Behaviors
Abstract
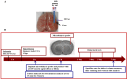
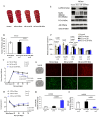
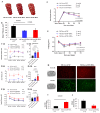
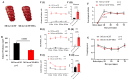
Ischemic stroke leads to cerebral ionic imbalance, increases acidosis, oxidative stress and release of glutamate and inflammatory mediators. Removing solute or stimulants from the ischemic core may block cell-damaging events and confer neuroprotection. In this study, we developed a minimally invasive therapeutic microdialysis (tMD) method, choosing to include serum albumin in the buffer because it is a multifunctional protein with osmotic properties. Aiming at the ischemic core, continuous perfusion of buffer supplemented with osmotic agents removes mediators of inflammation/cell damage/death from the lesion. This tMD treatment significantly removed the glutamate and zinc ions from the core, thereby reducing infarct volumes and affording high-grade neurobehavioral protection against ischemic stroke. The tMD treatment effectively protected neurons and reduced microglial activation. Furthermore, this tMD approach extended the therapeutic window to protect beyond 6 h after stroke onset. These findings support the potential clinical feasibility of applying tMD to patients with ischemic stroke, potentially without adverse effects.
Keywords: cerebral ischemia; microdialysis; neuroprotection; serum albumin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Feigin V.L., Owolabi M.O., World Stroke Organization-Lancet Neurology Commission Stroke Collaboration Group Pragmatic solutions to reduce the global burden of stroke: A World Stroke Organization-Lancet Neurology Commission. Lancet Neurol. 2023;22:1160–1206. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(23)00277-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

