Dried Spot Paradigm: Problems and Prospects in Proteomics
- PMID: 40332506
- PMCID: PMC12027537
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26083857
Dried Spot Paradigm: Problems and Prospects in Proteomics
Abstract
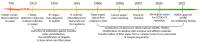
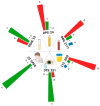
The analysis of biological fluids plays a crucial role in biomarker discovery, disease diagnostics, and precision medicine. Dried sample carriers-such as dried blood spots, dried plasma, serum, saliva, tears, and urine-have emerged as powerful tools, offering advantages in sample collection, storage, and transport, particularly in remote and resource-limited settings. Recent advances in proteomic methodologies have expanded the potential of these dried matrices, yet challenges related to protein stability, sensitivity, and standardization persist. This review critically examines the current state of proteomic investigations using dried biological fluids. Furthermore, we compare proteomics' progress in this field with other omics approaches, such as metabolomics, to contextualize its development and integration potential. While dried fluid proteomics is promising for non-invasive diagnostics and large-scale epidemiological studies, addressing technical limitations will be essential for its broader adoption in clinical and translational research.
Keywords: biomarker; diagnostics; dried sample; proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Approaching clinical proteomics: current state and future fields of application in fluid proteomics.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2009;47(6):724-44. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2009.167. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2009. PMID: 19527139 Review.
-
Towards reproducible MRM based biomarker discovery using dried blood spots.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 27;7:45178. doi: 10.1038/srep45178. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28345601 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomics of human biological fluids for biomarker discoveries: technical advances and recent applications.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2022 Feb;19(2):131-151. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2022.2070477. Epub 2022 May 5. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2022. PMID: 35466824 Review.
-
Proteomics and metabolomics characterizing the pathophysiology of adaptive reactions to the metabolic challenges during the transition from late pregnancy to early lactation in dairy cows.J Proteomics. 2018 Apr 30;178:92-106. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2017.10.010. Epub 2017 Oct 18. J Proteomics. 2018. PMID: 29055723 Review.
-
Multi-omics analysis from archival neonatal dried blood spots: limitations and opportunities.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2022 Jun 8;60(9):1318-1341. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2022-0311. Print 2022 Aug 26. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2022. PMID: 35670573 Review.
References
-
- Hannon W.H., Therrell B.L. Overview of the History and Applications of Dried Blood Samples. In: Li W., Lee M.S., editors. Dried Blood Spots. Wiley; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2014. pp. 1–15.
-
- O’Farrell B. Evolution in Lateral Flow–Based Immunoassay Systems. In: Wong R., Tse H., editors. Lateral Flow Immunoassay. Humana Press; Totowa, NJ, USA: 2009. pp. 1–33.
-
- Kiyaga C., Makoha C., Nkugwa I., Okiira C., Okwir R., Gebreab S.Z., Suarez P.R.-V., LaBrot B., Durán A.C. The Plasma Separation Card as a Novel Solution for Enhancing Central Laboratory Capability for HIV-1 Viral Load Monitoring in Limited-Access Settings. PLoS Glob. Public Health. 2023;3:e0002099. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0002099. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

