Neuroinflammation and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Recent Advances in Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines as Therapeutic Strategies
- PMID: 40332510
- PMCID: PMC12028049
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26083854
Neuroinflammation and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Recent Advances in Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines as Therapeutic Strategies
Abstract
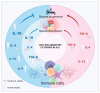
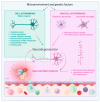
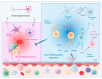
Neuroinflammation is an inflammatory response occurring within the central nervous system (CNS). The process is marked by the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, small-molecule messengers, and reactive oxygen species. Microglia and astrocytes are primarily involved in this process, while endothelial cells and infiltrating blood cells contribute to neuroinflammation when the blood-brain barrier (BBB) is damaged. Neuroinflammation is increasingly recognized as a pathological hallmark of several neurological diseases, including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and is closely linked to neurodegeneration, another key feature of ALS. In fact, neurodegeneration is a pathological trigger for inflammation, and neuroinflammation, in turn, contributes to motor neuron (MN) degeneration through the induction of synaptic dysfunction, neuronal death, and inhibition of neurogenesis. Importantly, resolution of acute inflammation is crucial for avoiding chronic inflammation and tissue destruction. Inflammatory processes are mediated by soluble factors known as cytokines, which are involved in both promoting and inhibiting inflammation. Cytokines with anti-inflammatory properties may exert protective roles in neuroinflammatory diseases, including ALS. In particular, interleukin (IL)-10, transforming growth factor (TGF)-β, IL-4, IL-13, and IL-9 have been shown to exert an anti-inflammatory role in the CNS. Other recently emerging immune regulatory cytokines in the CNS include IL-35, IL-25, IL-37, and IL-27. This review describes the current understanding of neuroinflammation in ALS and highlights recent advances in the role of anti-inflammatory cytokines within CNS with a particular focus on their potential therapeutic applications in ALS. Furthermore, we discuss current therapeutic strategies aimed at enhancing the anti-inflammatory response to modulate neuroinflammation in this disease.
Keywords: amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; cytokines; neuroinflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Senolytics: A Novel Strategy for Neuroprotection in ALS?Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 8;22(21):12078. doi: 10.3390/ijms222112078. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Erythropoietin modulates the immune-inflammatory response of a SOD1(G93A) transgenic mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).Neurosci Lett. 2014 Jun 27;574:53-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2014.05.001. Epub 2014 May 10. Neurosci Lett. 2014. PMID: 24820540
-
Neuroinflammation in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Role of Redox (dys)Regulation.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018 Jul 1;29(1):15-36. doi: 10.1089/ars.2017.7271. Epub 2017 Oct 16. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018. PMID: 28895473 Review.
-
Blood-CNS barrier dysfunction in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Proposed mechanisms and clinical implications.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2023 May;43(5):642-654. doi: 10.1177/0271678X231153281. Epub 2023 Jan 26. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2023. PMID: 36704819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New kid on the block: does histamine get along with inflammation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis?CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2015;14(5):677-86. doi: 10.2174/1871527314666150225143921. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2015. PMID: 25714965 Review.
Cited by
-
The IL-12 family cytokines in neurodegenerative diseases: dual roles in neurotoxicity and neuroprotection.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Aug 13. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01901-z. Online ahead of print. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40801981 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

