Neuronally Derived Extracellular Vesicles' Oligomeric and p129-α-Synuclein Levels for Differentiation of Parkinson's Disease from Essential Tremor
- PMID: 40332541
- PMCID: PMC12028296
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26083819
Neuronally Derived Extracellular Vesicles' Oligomeric and p129-α-Synuclein Levels for Differentiation of Parkinson's Disease from Essential Tremor
Abstract
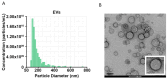
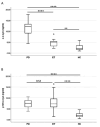
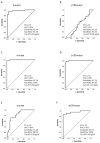
Clinical differentiation between Parkinson's disease (PD) and essential tremor (ET) may be challenging, highlighting the need for easily assessable diagnostic biomarkers. Neuronally derived extracellular vesicles (NDEVs) have been proposed as a peripheral matrix that can well recapitulate the cellular composition of neurons. We investigated the clinical usefulness of NDEV oligomeric and p129-α-synuclein levels in discriminating between patients with PD and those with ET. NDEV oligomeric and p129-α-synuclein species were assessed using an ELISA in 43 patients with PD, 21 patients with ET, and 45 healthy controls (HCs). NDEV oligomeric α-synuclein levels were significantly higher in PD in comparison with ET and HCs, while p129-α-synuclein values were significantly lower in HCs compared to other groups. By using a receiver operator characteristic (ROC) analysis, oligomeric-α-synuclein achieved an excellent classification performance in distinguishing PD from both ET and HCs (AUC: 0.976 and 0.997, respectively), while lower performance was obtained in differentiating ET from HCs (AUC: 0.85). On the other hand, p129-α-synuclein accurately discriminated both PD and ET from HCs (AUC: 0.997 and 0.952, respectively) but had very low performance in differentiating PD from ET (AUC: 0.47). Our study suggests that NDEV oligomeric α-synuclein is an accurate blood-derived biomarker to differentiate PD from ET, while p129-α-synuclein may be useful in distinguishing ET from HCs.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; essential tremor; neuronally derived extracellular vesicles; oligomeric α-synuclein; p129-α-synuclein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oligomeric α-synuclein and tau aggregates in NDEVs differentiate Parkinson's disease from atypical parkinsonisms.Neurobiol Dis. 2023 Jan;176:105947. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2022.105947. Epub 2022 Dec 5. Neurobiol Dis. 2023. PMID: 36481435
-
α-Synuclein species in plasma neuron-derived extracellular vesicles as biomarkers for iRBD.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2024 Nov;11(11):2891-2903. doi: 10.1002/acn3.52200. Epub 2024 Sep 18. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39291779 Free PMC article.
-
α-Synuclein in salivary extracellular vesicles as a potential biomarker of Parkinson's disease.Neurosci Lett. 2019 Mar 23;696:114-120. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2018.12.030. Epub 2018 Dec 21. Neurosci Lett. 2019. PMID: 30579996
-
α-Synuclein in Extracellular Vesicles: Functional Implications and Diagnostic Opportunities.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Apr;36(3):437-48. doi: 10.1007/s10571-015-0317-0. Epub 2016 Mar 18. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26993503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salivary alpha-synuclein as a biomarker for Parkinson's disease: a systematic review.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2019 Nov;126(11):1373-1382. doi: 10.1007/s00702-019-02062-4. Epub 2019 Aug 10. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2019. PMID: 31401695
References
-
- Bhatia K.P., Bain P., Bajaj N., Elble R.J., Hallett M., Louis E.D., Raethjen J., Stamelou M., Testa C.M., Deuschl G., et al. Consensus Statement on the classification of tremors. from the task force on tremor of the International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society. Mov. Disord. 2018;33:75–87. doi: 10.1002/mds.27121. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

