The Relationship Between Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, and Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index Markers and Response to Biological Therapy in Patients with Psoriasis
- PMID: 40332589
- PMCID: PMC12028229
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26083868
The Relationship Between Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, and Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index Markers and Response to Biological Therapy in Patients with Psoriasis
Abstract
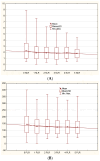
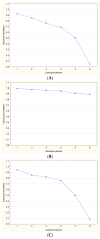
Plaque psoriasis is a chronic, immune-mediated inflammatory skin disease characterized by the formation of thick, scaly plaques. The disease is driven by dysregulation of the immune response, primarily involving T-helper cells, which create a persistent inflammatory environment. In recent years, several biomarkers reflecting systemic inflammation have been identified, including indices derived from a complete blood count, such as the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), and Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index (SII). The aim of our study was to explore the role of these markers in patients with psoriasis undergoing biological treatment. Medical records of 159 patients with plaque psoriasis receiving biologics were retrospectively reviewed. The NLR, PLR, and SII values were calculated from the hemograms of the patients. Additionally, demographic and psoriasis severity data were analyzed. During the 18-month follow-up, the mean NLR, PLR, SII, and CRP values were significantly decreased in comparison to the baseline (p < 0.05). No significant differences between anti-TNF, anti-IL-12/23, anti-IL-17, and anti-IL-23 drugs were identified (p > 0.05). The initial values of NLR, PLR, and SII were positively correlated with psoriasis severity. No relationship between the analyzed biomarkers and age, sex, psoriasis duration, and prior exposure to biological drugs was identified. CBC-derived biomarkers may be useful for monitoring inflammation reduction in psoriasis patients treated with biological drugs.
Keywords: biological therapy; neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio; psoriasis; systemic immune-inflammation index.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the inflammatory parameters as potential biomarkers of systemic inflammation extent and the disease severity in psoriasis patients.Arch Dermatol Res. 2024 May 24;316(6):229. doi: 10.1007/s00403-024-02972-8. Arch Dermatol Res. 2024. PMID: 38787405
-
Associations of novel complete blood count-derived inflammatory markers with psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Arch Dermatol Res. 2024 May 24;316(6):228. doi: 10.1007/s00403-024-02994-2. Arch Dermatol Res. 2024. PMID: 38787437
-
Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-lymphocyte ratio and mean platelet volume in Japanese patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: Response to therapy with biologics.J Dermatol. 2017 Oct;44(10):1112-1121. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.13875. Epub 2017 May 11. J Dermatol. 2017. PMID: 28493493
-
Are IL-17 inhibitors superior to IL-23 inhibitors in reducing systemic inflammation in moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis? A retrospective cohort study.Arch Dermatol Res. 2025 Jan 13;317(1):232. doi: 10.1007/s00403-024-03768-6. Arch Dermatol Res. 2025. PMID: 39804473
-
Pan-immune inflammation value and systemic inflammatory index as a measure of systemic inflammation in patients with psoriasis: A retrospective study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Mar 7;104(10):e41715. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041715. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40068069 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A nomogram-based clinical prediction model for adverse clinical outcomes in non-HIV Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia patients.BMC Pulm Med. 2025 May 17;25(1):238. doi: 10.1186/s12890-025-03700-2. BMC Pulm Med. 2025. PMID: 40382550 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reich A., Szepietowski J., Adamski Z., Chodorowska G., Kaszuba A., Krasowska D., Lesiak A., Maj J., Narbutt J., Osmola-Mankowska A., et al. Psoriasis. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Recommendations of the Polish Dermatological Society. Part II: Moderate to Severe Psoriasis. Dermatol. Rev. Przegląd Dermatol. 2018;105:329–357. doi: 10.5114/dr.2020.95259. - DOI
-
- Kimak-Pielas A., Robak E., Zajdel R., Zebrowska A. Demographics, Disease Characteristics, and Treatment Patterns of Patients with Plaque Psoriasis Treated with Biological Drugs: The Experience of a Single-Centre Study in Poland. J. Clin. Med. 2024;13:7647. doi: 10.3390/jcm13247647. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

