Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG) for Patients with Severe Neurotoxicity Associated with Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell (CAR-T) Therapy
- PMID: 40332772
- PMCID: PMC12028060
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26083904
Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG) for Patients with Severe Neurotoxicity Associated with Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell (CAR-T) Therapy
Abstract
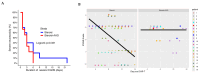
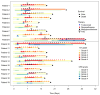
Severe immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS) occurs in about 30% of all patients with large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL) who are treated with axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel). There are currently limited treatment strategies other than the standard corticosteroids, and it is essential to find additional therapies to manage severe ICANS. We conducted a retrospective study of neurologic outcomes among patients who received axi-cel for LBCL from May 2015 to February 2019. We identified patients who developed severe ICANS and were treated with glucocorticoids followed by intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) (n = 9) or glucocorticoids alone (n = 10). There was no statistically significant difference in the time to resolution (TTR) of severe ICANS between groups; however, patients in the IVIG had more severe grades of ICANS with a lower performance status at baseline. The cumulative steroid days were 11.2 in the IVIG arm and 13.5 in the glucocorticoids-only arm. The use of IVIG for severe ICANS after axi-cel therapy was tolerable and safe and is generally recommended in the CAR-T setting in patients with hypogammaglobinemia. The use of IVIG as a potential therapeutic agent for severe ICANS can be further explored in future prospective studies.
Keywords: CAR-T; CAR-T-related encephalopathy syndrome; CRES; ICANS; IVIG; axicabtagene ciloleucel; neurotoxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
Sepideh Mokhtari, Michael D. Jain: Kite Pharma consultancy. Frederick L. Locke: Kite/Gilead: scientific advisor, research support; Celgene/BMS: scientific advisor, travel and lodging support; Novartis: scientific advisor; Allogene: scientific advisor; Wugen: scientific advisor; Calibr: scientific advisor; GammaDelta Therapeutics: scientific advisor; Cellular BioMedicine Group Inc: consultant, travel and lodging support. Moffitt Cancer Center holds patents in Frederick Locke’s name in the field of cellular immunotherapy, including CAR-T-cell therapy. Aleksandr Lazaryan: Sanofi: scientific advisor/consultant.
Figures

References
-
- Locke F.L., Ghobadi A., Jacobson C.A., Miklos D.B., Lekakis L.J., Oluwole O.O., Lin Y., Braunschweig I., Hill B.T., Timmerman J.M., et al. Long-term safety and activity of axicabtagene ciloleucel in refractory large B-cell lymphoma (ZUMA-1): A single-arm, multicentre, phase 1–2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20:31–42. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30864-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Neelapu S.S., Locke F.L., Bartlett N.L., Lekakis L.J., Miklos D.B., Jacobson C.A., Braunschweig I., Oluwole O.O., Siddiqi T., Lin Y., et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel CAR T-Cell Therapy in Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017;377:2531–2544. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1707447. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lee D.W., Santomasso B.D., Locke F.L., Ghobadi A., Turtle C.J., Brudno J.N., Maus M.V., Park J.H., Mead E., Pavletic S., et al. ASTCT Consensus Grading for Cytokine Release Syndrome and Neurologic Toxicity Associated with Immune Effector Cells. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019;25:625–638. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2018.12.758. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

