Immunogenicity and Safety of Influenza and COVID-19 Multicomponent Vaccine in Adults ≥50 Years: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 40332892
- PMCID: PMC12060023
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2025.5646
Immunogenicity and Safety of Influenza and COVID-19 Multicomponent Vaccine in Adults ≥50 Years: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: Uptake of recommended seasonal influenza and COVID-19 vaccines remains suboptimal.
Objective: To assess the immunogenicity and safety of an investigational mRNA-1083 vaccine against seasonal influenza and SARS-CoV-2 in adults 50 years and older.
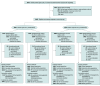
Design, setting, and participants: This phase 3, randomized, observer-blinded trial was conducted across 146 US sites in adults 50 years and older enrolled between October 19, 2023, and November 21, 2023. Data extraction was complete on April 9, 2024.
Interventions: Participants in 2 age cohorts (≥65 years and 50-64 years) were randomly assigned (1:1) to receive mRNA-1083 plus placebo or coadministered licensed quadrivalent seasonal influenza (≥65 years: high-dose quadrivalent inactivated influenza vaccine [HD-IIV4]; 50-64 years: standard-dose IIV4 [SD-IIV4]) and COVID-19 (all ages: mRNA-1273) vaccines.
Main outcomes and measures: The primary objectives were to demonstrate the noninferiority of humoral immune responses following mRNA-1083 vs comparators against vaccine-matched strains at day 29 and to evaluate the reactogenicity and safety of mRNA-1083. Secondary objectives included demonstration of superiority of humoral immune responses elicited by mRNA-1083 relative to comparators at day 29.
Results: Overall, 8015 participants were enrolled and vaccinated (4017 aged ≥65 y and 3998 aged 50-64 y). Among adults 65 years and older and 50 to 64 years, the median age was 70 and 58 years, 54.2% and 58.8% were female, 18.4% and 26.7% were Black or African American, and 13.9% and 19.3% were Hispanic or Latino, respectively. Noninferior immunogenicity of mRNA-1083 was demonstrated against all vaccine-matched influenza and SARS-CoV-2 strains based on lower bound of the 97.5% CI of the geometric mean ratio greater than 0.667 and lower bound of the 97.5% CI of the seroconversion/seroresponse rate difference greater than -10%. mRNA-1083 elicited higher immune responses than SD-IIV4 (50-64 years) for all 4 influenza strains and HD-IIV4 (≥65 years) for 3 influenza strains (A/H1N1, A/H3N2, B/Victoria) and against SARS-CoV-2 (all ages). Solicited adverse reactions were numerically higher in frequency and severity after mRNA-1083 vaccination than comparators in both age cohorts (≥65 y: 83.5% and 78.1%; 50-64 y: 85.2% and 81.8%); most were grade 1 or 2 in severity and of short duration. No safety concerns were identified.
Conclusions and relevance: In this study, mRNA-1083 met noninferiority criteria and induced higher immune responses than recommended standard care influenza (standard and high dose) and COVID-19 vaccines against all 4 influenza strains (among those ages 50-64 y), the 3 clinically relevant influenza strains (among those aged ≥65 y), and SARS-CoV-2 (all ages), with an acceptable tolerability and safety profile.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT06097273.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- GBD 2021 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators . Global incidence, prevalence, years lived with disability (YLDs), disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 371 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990-2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet. 2024;403(10440):2133-2161. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00757-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Vaccines against influenza: WHO position paper—May 2022. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 2022;97(19):185-208.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . RESP-NET Interactive Dashboard (2023-24 season). Updated June 7, 2024. Accessed April 8, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/resp-net/dashboard/index.html
-
- GBD 2021 Causes of Death Collaborators . Global burden of 288 causes of death and life expectancy decomposition in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990-2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet. 2024;403(10440):2100-2132. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00367-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Havers FP. COVID-19-associated hospitalizations among infants, children and adults—COVID-NET, January-August 2023. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. September 12, 2023. Accessed February 29, 2024. https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/132883
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

