Fermentation of Pediococcus pentosaceus JC30 Improves Phytochemical, Flavor Characteristics and Antioxidant Activity of Mulberry Leaves
- PMID: 40333611
- PMCID: PMC12029543
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30081703
Fermentation of Pediococcus pentosaceus JC30 Improves Phytochemical, Flavor Characteristics and Antioxidant Activity of Mulberry Leaves
Abstract
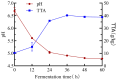
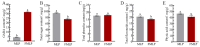
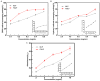
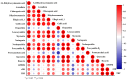
Mulberry leaves contain polysaccharides, phenols, alkaloids, and other active ingredients which have medicinal and edible value. In this study, fermented mulberry leaf powder was prepared by solid-state fermentation using Pediococcus pentosaceus JC30. The effects of the fermentation on the phytochemical, flavor characteristics, phenolics, and antioxidant activity of mulberry leaves were studied. The results showed that the content of γ-aminobutyric acid in fermented mulberry leaf powder (FMLP) increased by 6.73-fold and the content of phytic acid decreased by 11.16%. Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q-TOF-MS) analysis showed that the fermentation of Pediococcus pentosaceus JC30 altered the phenolic composition of mulberry leaves, increasing the total free phenolic content by 88.43%. In particular, the contents of free phenols such as leucocyanidin, myricetin, and quercetin increased significantly and were positively correlated with antioxidant capacity. The fermentation of Pediococcus pentosaceus JC30 significantly enhanced the scavenging ability of DPPH free radicals, hydroxyl radicals, and the total reducing ability of mulberry leaves. Gas chromatography ion mobility spectrometry (GC-IMS) analysis showed that FMLP has an intense fruity and floral aroma, while having less grassy and earthy odor. The fermentation improved the phytochemical, flavor, and nutritional value of mulberry leaves, which provides more possibilities for the development of mulberry leaf products outside the sericulture industry.
Keywords: Pediococcus pentosaceus JC30; antioxidant activity; bioactive compounds; mulberry leaves; volatile compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pediococcus pentosaceus JS35 improved flavor, metabolic profile of fermentation supernatant of mulberry leaf powder and increased its antioxidant capacity.Front Nutr. 2025 Mar 4;12:1551689. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1551689. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40104817 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation on Antioxidant Activity and Different Metabolites of Mulberry (Morus spp.) Leaves Depending on the Harvest Months by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS with Multivariate Tools.Molecules. 2023 Feb 17;28(4):1947. doi: 10.3390/molecules28041947. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36838934 Free PMC article.
-
Mixed Mulberry Fruit and Mulberry Leaf Fermented Alcoholic Beverages: Assessment of Chemical Composition, Antioxidant Capacity In Vitro and Sensory Evaluation.Foods. 2022 Oct 8;11(19):3125. doi: 10.3390/foods11193125. Foods. 2022. PMID: 36230199 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-function relationship and biological activity of polysaccharides from mulberry leaves: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 May;268(Pt 1):131701. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131701. Epub 2024 Apr 19. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38643920 Review.
-
Research Progress on Phytochemicals from Mulberry with Neuroprotective Effects: A Review.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 May 8;18(5):695. doi: 10.3390/ph18050695. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40430516 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li R., Wang C., Chen Y., Li N., Wang Q., Zhang M., He C., Chen H. A combined network pharmacology and molecular biology approach to investigate the active ingredients and potential mechanisms of mulberry (Morus alba L.) leaf on obesity. Phytomedicine. 2021;92:153714. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153714. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gao T.Q., Chen J.L., Xu F., Wang Y.L., Zhao P.P., Ding Y.F., Han Y.B., Yang J., Tao Y. Mixed mulberry fruit and mulberry leaf fermented alcoholic beverages: Assessment of chemical composition, antioxidant capacity in vitro and sensory evaluation. Foods. 2022;11:3125. doi: 10.3390/foods11193125. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang N.W., Xiong Y., Wang X.K., Guo L.N., Lin Y.L., Ni K.K., Yang F.Y. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum on fermentation quality and anti-nutritional factors of paper mulberry silage. Fermentation. 2022;8:144. doi: 10.3390/fermentation8040144. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- SJCX24_2564/Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province
- SNG2022029/Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Project of Suzhou City
- NY2024018/Zhenjiang Key R&D Program Project
- BK20230529/Jiangsu Provincial Natural Science Foundation Youth Science Fund
- SKLTCM2022020/Open Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Southwestern Chinese Medicine Resources
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

