Enhanced Infrared Shielding Function in ATO-Doped Polymer-Dispersed Liquid Crystal Films
- PMID: 40333711
- PMCID: PMC12029530
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30081730
Enhanced Infrared Shielding Function in ATO-Doped Polymer-Dispersed Liquid Crystal Films
Abstract
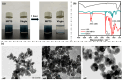
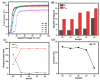
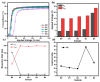
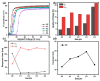
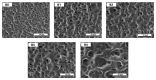
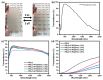
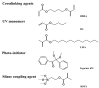
The enhanced infrared shielding function of antimony tin oxide (ATO)-doped polymer-dispersed liquid crystal (PDLC) film enables its use for smart windows, because it can switch between transparent and scattered states, which can protect people's privacy. When PDLC film is used for a building's doors and windows or external walls, we hope that it can have a higher infrared shielding capability, in order to reduce the indoor temperature affected by solar irradiation, so as to reduce the energy consumption caused by refrigeration equipment. However, the infrared shielding capability of the existing PDLC is far from sufficient. In this work, modified ATO nanoparticles of different sizes were introduced into the PDLC system to improve its infrared shielding capability. It was found that when the ATO particle size is 20 nm and the doping content is 0.6 wt%, the modified PDLC sample provides optimal infrared shielding function while maintaining excellent electro-optical properties.
Keywords: ATO; PDLC; infrared shielding; nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Spectrum-Tailored Polymer Dispersed Liquid Crystal Film for Energy-Saving Smart Windows.Small. 2025 Feb;21(5):e2409347. doi: 10.1002/smll.202409347. Epub 2024 Dec 17. Small. 2025. PMID: 39690837
-
Electro-Optical Characteristics of Polymer Dispersed Liquid Crystal Doped with MgO Nanoparticles.Molecules. 2022 Oct 26;27(21):7265. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217265. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36364092 Free PMC article.
-
Visible and infrared optical modulation of PSLC smart films doped with ATO nanoparticles.Dalton Trans. 2021 Jul 27;50(29):10033-10040. doi: 10.1039/d1dt01575c. Dalton Trans. 2021. PMID: 34231593
-
Optical microscopy studies of dynamics within individual polymer-dispersed liquid crystal droplets.Acc Chem Res. 2005 Feb;38(2):137-45. doi: 10.1021/ar040106p. Acc Chem Res. 2005. PMID: 15709733 Review.
-
A Comprehensive Review on Polymer-Dispersed Liquid Crystals: Mechanisms, Materials, and Applications.ACS Mater Au. 2024 Nov 27;5(1):88-114. doi: 10.1021/acsmaterialsau.4c00122. eCollection 2025 Jan 8. ACS Mater Au. 2024. PMID: 39802145 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang L., Bisoyi H.K., Zheng Z., Gutierrez-Cuevas K.G., Singh G., Kumar S., Bunning T.J., Li Q. Stimuli-directed self-organized chiral superstructures for adaptive windows enabled by mesogen-functionalized graphene. Mater. Today. 2017;20:230–237. doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2017.04.028. - DOI
-
- Khandelwal H., Schenning A.P.H.J., Debije M.G. Infrared Regulating Smart Window Based on Organic Materials. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017;7:1602209. doi: 10.1002/aenm.201602209. - DOI
-
- Brzezicki M. A Systematic Review of the Most Recent Concepts in Smart Windows Technologies with a Focus on Electrochromics. Sustainability. 2021;13:9604. doi: 10.3390/su13179604. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 2023YFB3812800/the National Key R&D Program of China
- U22A20163/the National Natural Science Foundation of China Joint Fund
- 52202081,51921002, 51927806/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2023QT01/the Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by JXAST
- ZC2023011/the Science Research Project of Hebei Education Department
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

