Comparative Evaluation of Cytotoxic and Apoptotic Effects of Natural Compounds in SH-SY5Y Neuroblastoma Cells in Relation to Their Physicochemical Properties
- PMID: 40333735
- PMCID: PMC12029500
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30081742
Comparative Evaluation of Cytotoxic and Apoptotic Effects of Natural Compounds in SH-SY5Y Neuroblastoma Cells in Relation to Their Physicochemical Properties
Abstract
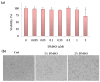
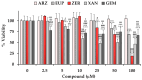
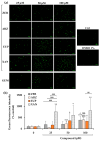
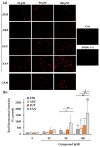
The cytotoxic and apoptotic properties of four bioactive natural compounds, the prenylated α-pyronephloroglucinol heterodimer arzanol (ARZ), the methoxylated flavones eupatilin (EUP) and xanthomicrol (XAN), and the sesquiterpene zerumbone (ZER), were compared in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells to assess their potential as neuroblastoma-specific therapeutics. EUP, XAN, and ZER (2.5-100 μM) exerted marked significant cytotoxicity (MTT assay) and morphological changes after 24 h of incubation, following the order XAN > ZER > EUP > ARZ (no toxic effect). The propidium iodide fluorescence assay (PI, red fluorescence) and NucView® 488 assay (NV, green fluorescence) evidenced a significant increase in the apoptotic cell number, vs. controls, in SH-SY5Y cells pre-incubated for 2 h with the compounds, in the following order of apoptotic potency: XAN > EUP > ZER > ARZ. The PubChem database and freely accessible web tools SwissADME, pkCSM-pharmacokinetics, and SwissTargetPrediction were used to assess the physicochemical/pharmacokinetic properties and potential protein targets of the compounds. At 50 μM, a positive correlation (r = 0.917) between values of % viability reduction and % human intestinal absorption (bioavailability) was observed, indicating a marked contribution of compound membrane permeability to cytotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells. The capacity of compounds to induce apoptosis emerged as inversely correlated to the computed lipophilicity (r = -0.885).
Keywords: SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma; apoptosis; arzanol; cytotoxicity; eupatilin; xanthomicrol; zerumbone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Protective Effect of Arzanol against H2O2-Induced Oxidative Stress Damage in Differentiated and Undifferentiated SH-SY5Y Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 5;25(13):7386. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137386. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000492 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Evaluation of Anticancer Activity of Natural Methoxylated Flavones Xanthomicrol and Eupatilin in A375 Skin Melanoma Cells.Life (Basel). 2024 Feb 26;14(3):304. doi: 10.3390/life14030304. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38541630 Free PMC article.
-
Zerumbone Induces Apoptosis in Breast Cancer Cells by Targeting αvβ3 Integrin upon Co-Administration with TP5-iRGD Peptide.Molecules. 2019 Jul 13;24(14):2554. doi: 10.3390/molecules24142554. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31337024 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-proliferative and cytotoxic activities of the flavonoid isoliquiritigenin in the human neuroblastoma cell line SH-SY5Y.Chem Biol Interact. 2019 Feb 1;299:77-87. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2018.11.022. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Chem Biol Interact. 2019. PMID: 30502331
-
Ethyl acetate extract of germinated brown rice attenuates hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells: role of anti-apoptotic, pro-survival and antioxidant genes.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2013 Jul 17;13:177. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-13-177. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2013. PMID: 23866310 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
TPP-Based Nanovesicles Kill MDR Neuroblastoma Cells and Induce Moderate ROS Increase, While Exerting Low Toxicity Towards Primary Cell Cultures: An In Vitro Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 22;26(11):4991. doi: 10.3390/ijms26114991. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40507803 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rosa A., Deiana M., Atzeri A., Corona G., Incani A., Melis M.P., Appendino G., Dessì M.A. Evaluation of the antioxidant and cytotoxic activity of arzanol, a prenylated alpha-pyrone-phloroglucinol etherodimer from Helichrysum italicum subsp. microphyllum. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2007;165:117–126. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2006.11.006. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

