Modulation of Tumor Metabolism in Acute Leukemia by Plant-Derived Polymolecular Drugs and Their Effects on Mitochondrial Function
- PMID: 40333775
- PMCID: PMC12029889
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30081783
Modulation of Tumor Metabolism in Acute Leukemia by Plant-Derived Polymolecular Drugs and Their Effects on Mitochondrial Function
Abstract
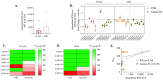
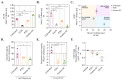
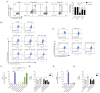
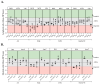
The analysis of tumor metabolism offers promising opportunities for developing new therapeutic strategies. Plant-derived polymolecular drugs can regulate cellular metabolism, making them potential candidates for treatment. This study examined the metabolic effects of plant-derived polymolecular drugs-P2Et, Anamu-SC, and Esperanza-on leukemic cell lines (lymphoid and myeloid types) and primary leukemic blasts. The metabolic analysis included oxidative status, glucose consumption, extracellular acidification, oxygen consumption, mitochondrial dynamics, and untargeted metabolomics. Additionally, the effect of co-treatment with conventional chemotherapeutic drugs was investigated. Results showed that P2Et and Anamu-SC reduced the viability and proliferation of all tumor cell lines, exhibiting antioxidant effects. Anamu-SC decreased reactive oxygen species levels in lymphoid tumor cells. Mitochondrial activity was selectively affected by the plant-derived polymolecular drugs, with Anamu-SC and Esperanza causing more significant, potentially reversible damage compared to P2Et. Anamu-SC and Esperanza increased levels of phosphatidylcholines and carnitines. The co-administration of plant-derived polymolecular drugs with chemotherapeutics improved the cytostatic efficacy of cytarabine. In conclusion, this research highlights the promising pharmacological activity of Anamu-SC and Esperanza as mitocans for the treatment of acute leukemia. The study emphasizes the practical significance of combining plant-derived polymolecular drugs with conventional chemotherapeutics to enhance their cytostatic efficacy.
Keywords: acute leukemia; chemotherapy; metabolism; mitocans; plant-derived polymolecular drugs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Swerdlow S.H., Campoo E., Lee N., Jaffe E.S., Pileri S.A., Stein H., Thiele J. WHO Classification of Tumors for Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. International Agency for Research on Cancer; Lyon, France: 2017.
-
- Sriskanthadevan S., Jeyaraju D.V., Chung T.E., Prabha S., Xu W., Skrtic M., Jhas B., Hurren R., Gronda M., Wang X., et al. AML cells have low spare reserve capacity in their respiratory chain that renders them susceptible to oxidative metabolic stress. Blood. 2015;125:2120–2130. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-08-594408. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

