Molecular-Based Nanoplatform Leads to the Formation of a Self-Indicating Responsive Drug Delivery System
- PMID: 40333797
- PMCID: PMC12029280
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30081782
Molecular-Based Nanoplatform Leads to the Formation of a Self-Indicating Responsive Drug Delivery System
Abstract
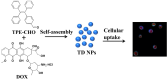
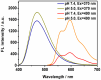
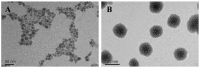
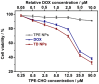
We report the design and biological evaluation of a nanoplatform featuring controllable aggregation-induced emission (AIE) behavior. The free rotation of benzene rings (4-(1,2,2-triphenylvinyl) benzaldehyde) largely suppresses fluorescence in the pure organic phase. However, water-induced molecular aggregation enhances the fluorescence signal. The delivery system follows the membrane-cytoplasm-nucleus route and it leads to apoptosis in two cancer cells (U937 cells and Hela cells). The AIE moiety accumulates in the cytoplasm, emitting a bright-blue signal, but the anticancer drug doxorubicin selectively targets the nucleus with unique red emission. The current noninvasive method with DOX-triggered apoptosis holds promise for tumor diagnosis and real-time imaging.
Keywords: cellular imaging; fluorescence; nanoplatform; therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Nanoplatform based on GSH-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for cancer therapy and mitochondrial targeted imaging.Mikrochim Acta. 2021 Apr 6;188(5):154. doi: 10.1007/s00604-021-04810-4. Mikrochim Acta. 2021. PMID: 33821295
-
Doxorubicin-loaded functionalized selenium nanoparticles for enhanced antitumor efficacy in cervical carcinoma therapy.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020 Jan;106:110100. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2019.110100. Epub 2019 Aug 21. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020. PMID: 31753388
-
Graphene quantum dots-gated hollow mesoporous carbon nanoplatform for targeting drug delivery and synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Oct 4;13:5991-6007. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S175934. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30323587 Free PMC article.
-
Thermal and pH responsive polymer-tethered multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles for targeted delivery of anticancer drug.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013 May;5(9):3884-93. doi: 10.1021/am400572b. Epub 2013 Apr 23. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013. PMID: 23551195
-
Self-Indicating Polymer Prodrug Nanoparticles for pH-Responsive Drug Delivery in Cancer Cells and Real-Time Monitoring of Drug Release.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2024 Sep 16;7(9):5810-5822. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.4c00878. Epub 2024 Aug 26. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2024. PMID: 39186444 Review.
References
-
- Chandana M., Manasi D., Jagat R.K., Sanjeeb K.S. Receptor Mediated Tumor Targeting: An Emerging Approach for Cancer Therapy. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2011;8:45–58. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

