Influence of Partial Disentanglement of Macromolecules on the Rheological, Thermal, and Mechanical Properties of Polypropylene-Polyethylene Blends
- PMID: 40333829
- PMCID: PMC12029187
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30081786
Influence of Partial Disentanglement of Macromolecules on the Rheological, Thermal, and Mechanical Properties of Polypropylene-Polyethylene Blends
Abstract
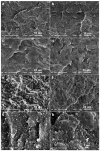
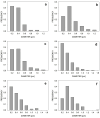
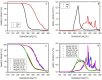
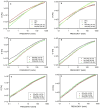
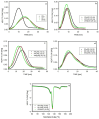
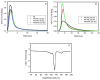
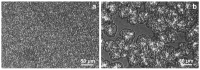
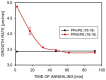
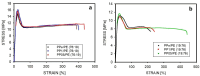
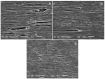
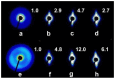
The properties of compatibilized blends of polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP), having reduced macromolecular entanglements, were studied. The density of PP macromolecular entanglements was controlled by prior disentangling in solution. The polymer ratio in the blend was 4:1 or 1:4. An ethylene-octene copolymer was used as a compatibilizer. The melt blending process resulted in good dispersion of the minority component, with slightly larger inclusions when more disentangled PP was used. Rheological studies confirmed the achievement of different entanglement densities of PP macromolecules in the blends. The partial disentanglement did not affect the thermal stability of the blends. During the isothermal crystallization studies, faster growth of PP spherulites was observed in the blend with reduced entanglements, which also influenced the entire crystallization process. The recovery time of equilibrium entanglement was investigated and it turned out to be 45 min if the blend was annealed at 190 °C, which was shorter than in the analogous homopolymer. Studies of tensile properties showed that in blends with a majority share of polyethylene, the elongation at break increased with the disentanglement of the minority component, due to better bonding of the blend components and thus the reduction in microcavitation.
Keywords: crystallization; entanglements; polypropylene–polyethylene blends.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Berry G.C., Fox T.G. The viscosity of polymers and their concentrated solutions. Adv. Polym. Sci. 1968;5:261–357. doi: 10.1007/BFb0050985. - DOI
-
- Fetters L.J., Lohse D.J., Richter D., Witten T.A., Zirkel A. The connection between polymer molecular weight, density, chain dimensions, and melt viscoelastic properties. Macromolecules. 1994;27:4639–4647. doi: 10.1021/ma00095a001. - DOI
-
- Pawlak A. The Entanglements of Macromolecules and Their Influence on the Properties of Polymers. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2019;220:1900043. doi: 10.1002/macp.201900043. - DOI
-
- Wang X.H., Liu R., Wu M., Wang Z., Huang Y. Effect of chain disentanglement on melt crystallization behavior of isotactic polypropylene. Polymer. 2009;50:5824–5827. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2009.10.002. - DOI
-
- Eckstein A., Suhm J., Friedrich C., Maier R., Sassmannshausen J., Bochmann M., Mulhaupt R. Determination of Plateau Moduli and Entanglement Molecular Weights of Isotactic, Syndiotactic, and Atactic Polypropylenes Synthesized with Metallocene Catalysts. Macromolecules. 1998;31:1335–1340. doi: 10.1021/ma971270d. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

