Role of Saponins from Platycodon grandiflorum in Alzheimer's Disease: DFT, Molecular Docking, and Simulation Studies in Key Enzymes
- PMID: 40333841
- PMCID: PMC12029169
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30081812
Role of Saponins from Platycodon grandiflorum in Alzheimer's Disease: DFT, Molecular Docking, and Simulation Studies in Key Enzymes
Abstract
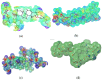
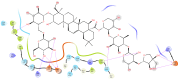
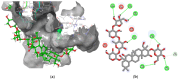
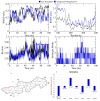
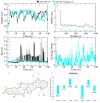
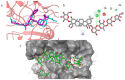
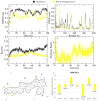
Alzheimer's disease (AD), one of the neurodegenerative disorders, afflicts negatively across the whole world. Due to its complex etiology, no available treatments are disease-altering. This study aimed to explore isolated saponins profiles from Platycodon grandiflorum in the binding pockets of six target proteins of AD using computational and quantum chemistry simulations. Initially, saponin compounds were docked to AD enzymes, such as GSK-3β and synapsin I, II, and III. The subsequent research from MD simulations of the best three docked compounds (polygalacin D2, polygalacin D, and platycodin D) suggested that their profiles match with the binding of standard active drugs like ifenprodil and donepezil to the six enzymes. Moreover, analyzing DFT quantum calculations of top-scoring compounds fully unravels their electronic and quantum properties and potential in anti-AD. The subtle differences between polygalacin D and D2, and platycodin D, were studied at the level of theory DFT/B3LYP, showing that the electron-donating effect of the hydroxy ethyl group in platycodin D rendering this compound of moderate electrophilicity and reactivity. Polygalacin D2 diglucoside substituent in position-2 contributed to its best binding and intermolecular interactions more than polygalacin D and prosapogenin D, which acted as the negative decoy drug.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s; Platycodon; density functional theory; molecular dynamics simulations; saponins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Better M.A. 2023 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2023;19:1598–1695. - PubMed
-
- Limantoro J., de Liyis B.G., Sutedja J.C. Akt signaling pathway: A potential therapy for Alzheimer’s disease through glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta inhibition. Egypt. J. Neurol. Psychiatry Neurosurg. 2023;59:147. doi: 10.1186/s41983-023-00751-2. - DOI
-
- Hampel H., Mesulam M.M., Cuello A.C., Farlow M.R., Giacobini E., Grossberg G.T., Khachaturian A.S., Vergallo A., Cavedo E., Snyder P.J., et al. The cholinergic system in the pathophysiology and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain. 2018;141:1917–1933. doi: 10.1093/brain/awy132. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

