Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) as Alternative Sustainable Media for the Extraction and Characterization of Bioactive Compounds from Winemaking Industry Wastes
- PMID: 40333869
- PMCID: PMC12029248
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30081855
Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) as Alternative Sustainable Media for the Extraction and Characterization of Bioactive Compounds from Winemaking Industry Wastes
Abstract
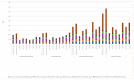
The increasing pollution and wastage of food and byproducts from agro-industrial production is an increasingly worrying issue. Grape is one of the most diffused fruit crops cultivated, and grape pomace is the main solid byproduct obtained in the winemaking process; interestingly, it is rich in health-beneficial bioactive molecules. In order to recover these molecules, in this work, a green method has been developed, considering two grape pomaces from different cultivars, namely, Petit Verdot and Cabernet Sauvignon. The extraction procedure, as the first step of this process, was carried out with seven selected deep eutectic solvents (DESs). Then, analysis using HPLC-DAD allowed the detection and quantification of eight out of fifteen different phenolic compounds under examination in the extracts produced, including three quercetin glucosides. The evaluation of antioxidant activity, through the DPPH photometric assay, led to the selection of choline chloride/urea 1:2 + 40% water DES extracts as the extracts with the most promising results. Moreover, significant antibacterial activity was also achieved, in particular, for the betaine/lactic acid 1:4 + 40% water DES extract. Further studies will employ this method for numerous cultivars of grape pomaces with the ambitious aim of the production of polyphenol-enriched food and feed supplements.
Keywords: antimicrobials; antioxidants; deep eutectic solvents (DESs); green chemistry; green extraction methods; winemaking industry wastes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Muchhadiya R.M., Gohil B., Yadahalli V., HM A.U.R., Siddiqua A., Khayum A., Behera H.S., Kumar S. Feeding the world: Agronomic innovations to meet the challenges of a growing population. Int. J. Res. Agron. 2024;7:790–802. doi: 10.33545/2618060X.2024.v7.i7j.1133. - DOI
-
- Roselli V., Pugliese G., Leuci R., Brunetti L., Gambacorta L., Tufarelli V., Piemontese L. Green Methods to Recover Bioactive Compounds from Food Industry Waste: A Sustainable Practice from the Perspective of the Circular Economy. Molecules. 2024;29:2682. doi: 10.3390/molecules29112682. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Freitas L.C., Barbosa J.R., da Costa A.L.C., Bezerra F.W.F., Pinto R.H.H., de Carvalho Junior R.N. From waste to sustainable industry: How can agro-industrial wastes help in the development of new products? Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021;169:105466. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.105466. - DOI
-
- Vastolo A., Calabrò S., Cutrignelli M.I. A review on the use of agro-industrial CO-products in animals’ diets. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2022;21:577–594. doi: 10.1080/1828051X.2022.2039562. - DOI
-
- Brunetti L., Leuci R., Colonna M.A., Carrieri R., Celentano F.E., Bozzo G., Loiodice F., Selvaggi M., Tufarelli V., Piemontese L. Food Industry Byproducts as Starting Material for Innovative, Green Feed Formulation: A Sustainable Alternative for Poultry Feeding. Molecules. 2022;27:4735. doi: 10.3390/molecules27154735. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

