Exploring the accuracy of the Xpert MTB/RIF assay in detecting lymph node tuberculosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40333873
- PMCID: PMC12057916
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0321507
Exploring the accuracy of the Xpert MTB/RIF assay in detecting lymph node tuberculosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The Xpert MTB/RIF assay has exhibited high diagnostic efficiency in detecting lymph node tuberculosis (LNTB). However, different gold standards and types of LNTB specimens may impact Xpert's diagnostic accuracy. This meta-analysis compared the performance of Xpert MTB/RIF on fine needle aspiration (FNA) and tissue samples against that of culture and composite reference standards (CRS) for LNTB diagnosis. In addition, we further reported the diagnostic accuracy of the Xpert MTB/RIF assay in identifying LNTB in different age groups and rifampicin resistance in LNTB patients.
Methods: A systematic search of Embase, Cochrane Library, PubMed, Web of Science, and Scopus up to October 26, 2023, was conducted. Studies comparing Xpert MTB/RIF with culture and CRS were selected. Meta-analyses and meta-regression were performed using Stata and Meta Disc software.
Results: In 9 studies, Xpert MTB/RIF was compared with CRS, while in 24 studies, it was compared with culture. The sensitivity and specificity of the Xpert MTB/RIF test were 85% and 97%, respectively, against CRS and 85% and 78%, respectively, against culture. FNA sensitivity and specificity were 93% and 88% respectively against CRS and 87% and 77% respectively against culture. For tissue samples, the sensitivity and specificity were 74% and 100%, respectively, against CRS and 74% and 77%, respectively, against culture. For the adult cohort (>14 years), the sensitivity and specificity of FNA samples were 80% and 75% against culture and 85% and 88% respectively against CRS. The pooled sensitivity and specificity of Xpert for detecting rifampicin resistance were 90% and 99% respectively.
Conclusion: Xpert MTB/RIF demonstrated excellent accuracy for diagnosing LNTB and rifampicin resistance, with FNA samples outperforming tissue samples acquired through biopsy and CRS as superior to culture standards.
Copyright: © 2025 Chen et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
NO authors have competing interests.
Figures
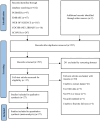




References
-
- W.H. Organization(WHO). Global Tuberculosis Report. 2019.
-
- Lewinsohn DM, Leonard MK, LoBue PA, Cohn DL, Daley CL, Desmond E, et al. Official American Thoracic Society/Infectious Diseases Society of America/Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Clinical Practice Guidelines: diagnosis of tuberculosis in adults and children. Clin Infect Dis. 2017;64(2):111–5. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciw778 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boehme CC, Nicol MP, Nabeta P, Michael JS, Gotuzzo E, Tahirli R, et al. Feasibility, diagnostic accuracy, and effectiveness of decentralised use of the Xpert MTB/RIF test for diagnosis of tuberculosis and multidrug resistance: a multicentre implementation study. Lancet. 2011;377(9776):1495–505. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60438-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

