Effects of heat reflux extraction on the content, antioxidant, and immune activity of polyphenols and flavonoids from hempseed threshing residues
- PMID: 40333885
- PMCID: PMC12057896
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0322134
Effects of heat reflux extraction on the content, antioxidant, and immune activity of polyphenols and flavonoids from hempseed threshing residues
Abstract
Objective: Hempseed threshing residues are rich in phytochemicals such as polyphenols and flavonoids. Phenolic and flavonoid compounds have been associated with antioxidant, antibacterial and anticancer activities. The re-use of the hempseed threshing residues as value-added materials is, not only cost-saving, but also environmentally beneficial. It is therefore important to develop an effective method for extraction of phenolic compounds and flavonoids from hempseed threshing residues.
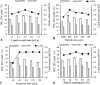
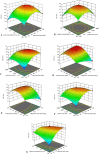
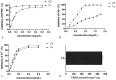
Methods: In this investigation, the extraction of phenolic constituents and flavonoids from hempseed threshing residues using heat reflux extraction (HRE) were optimized through response surface methodology (RSM). Four HRE parameters to enhance the yield of crude extracts (CE), total phenolic content (TPC), and total flavonoids content (TFC) were evaluated. Additionally, the study evaluated the chemical compounds, antioxidant characteristics of the extracts, and the immune activity of the extracts was assessed by quantifying the levels of inflammatory cytokines, specifically IL-6, IL-10, and TNF-α.
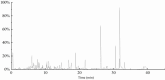
Results: The best extraction parameters were determined as: for the extraction time of 69.71 min, a liquid-solid proportion of 5.12:1, a particle size of 1150 µm, and an ethanol concentration of 69.60%. Under these optimized conditions, the yields for CE, TPC, and TFC were 4.74%, 27.54%, and 16.02% respectively. The data conformed well to multiple regression models, showing that these extraction parameters markedly influence the yields of CE, TPC, and TFC. Most of the compounds found may belong to the class of polyphenol and flavonoids. Cellular assays indicated that extracts from hempseed threshing residue notably reduced pro-inflammatory factors (TNF-α, IL-6) and increased anti-inflammatory factors (IL-10) in RAW 264.7 cells.
Conclusion: This research lays a theoretical foundation for extracting polyphenols and flavonoids from hempseed threshing residue and for the comprehensive assessment of antioxidant and immune-enhancing products. However, the antioxidant and immune activity of hempseed threshing residues extracts under physiological conditions in vivo, and the relevant mechanism should be further studied.
Copyright: © 2025 Li et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extraction, purification, in vitro antioxidant and cytoprotective ability of oligostilbenes from paeonia seeds threshing residues.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 11;20(6):e0325485. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0325485. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40498758 Free PMC article.
-
Flavonoid/Polyphenol Ratio in Mauritia flexuosa and Theobroma grandiflorum as an Indicator of Effective Antioxidant Action.Molecules. 2021 Oct 25;26(21):6431. doi: 10.3390/molecules26216431. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34770839 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of flavonoids, polyphenols and antioxidant activity of Tephrosia purpurea: a seasonal study.J Integr Med. 2016 Nov;14(6):447-455. doi: 10.1016/S2095-4964(16)60276-5. J Integr Med. 2016. PMID: 27854196
-
Plant-Derived Compounds in Hemp Seeds (Cannabis sativa L.): Extraction, Identification and Bioactivity-A Review.Molecules. 2024 Dec 31;30(1):124. doi: 10.3390/molecules30010124. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39795183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmentally Friendly Methods for Flavonoid Extraction from Plant Material: Impact of Their Operating Conditions on Yield and Antioxidant Properties.ScientificWorldJournal. 2020 Aug 28;2020:6792069. doi: 10.1155/2020/6792069. eCollection 2020. ScientificWorldJournal. 2020. PMID: 32908461 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Attard TM, Bainier C, Reinaud M, Lanot A, McQueen-Mason SJ, Hunt AJ. Utilisation of supercritical fluids for the effective extraction of waxes and Cannabidiol (CBD) from hemp wastes. Ind Crops Prod. 2018;112:38–46. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.10.045 - DOI
-
- Glivar T, Eržen J, Kreft S, Zagožen M, Čerenak A, Čeh B, et al.. Cannabinoid content in industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) varieties grown in Slovenia. Ind Crops Prod. 2020;145:112082. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.112082 - DOI
-
- Visković J, Dunđerski D, Adamović B, Jaćimović G, Latković D, Vojnović Đ. Toward an environmentally friendly future: an overview of biofuels from corn and potential alternatives in hemp and cucurbits. Agronomy. 2024;14(6):1195. doi: 10.3390/agronomy14061195 - DOI
-
- Grijó DR, Piva GK, Osorio IV, Cardozo-Filho L. Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) seed oil extraction with pressurized n-propane and supercritical carbon dioxide. J Supercrit Fluids. 2019;143:268–74. doi: 10.1016/j.supflu.2018.09.004 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

