Development of Fucoxanthin-Enriched Yogurt Using Nanoliposomal Carriers: A Strategy for Functional Dairy Products with Antioxidant and Erythroprotective Benefits
- PMID: 40333899
- PMCID: PMC12029523
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30081854
Development of Fucoxanthin-Enriched Yogurt Using Nanoliposomal Carriers: A Strategy for Functional Dairy Products with Antioxidant and Erythroprotective Benefits
Abstract
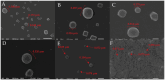
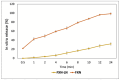
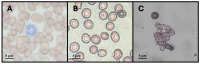
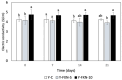
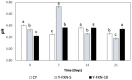
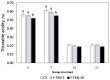
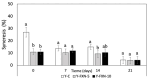
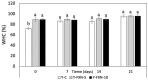
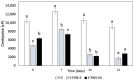
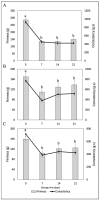
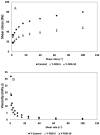
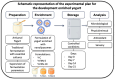
In pursuing functional foods that promote health, nanoliposomal carriers have been used to enhance the stability and functionality of dairy products such as yogurt, promising therapeutic benefits. This study aimed to evaluate the impact of fucoxanthin-loaded nanoliposomes in yogurt on its antioxidant, physicochemical, and rheological properties under cold storage (21 days). Fucoxanthin-loaded nanoliposomes were prepared using the ultrasonic film dispersion technique and added at concentrations of 0%, 5%, and 10% in the yogurt (Y-C, Y-FXN-5, Y-FXN-10). Homogeneous and uniform nanoliposomes (98.28 nm) were obtained, preserving their integrity and functionality and ensuring the prolonged release and bioavailability of fucoxanthin. Y-FXN-10 maintained the highest antioxidant activity according to the DPPH (52.96%), ABTS (97.97%), and FRAP (3.16 mmol ET/g) methods. This formulation exhibited enhanced erythroprotective potential, inhibiting hemolysis, photohemolysis, and heat-induced hemolysis. However, viscosity and firmness decreased, affecting the texture and appearance. Sensory properties such as the color, flavor, aftertaste, texture, and overall acceptance improved with the 10% fucoxanthin-enriched yogurt formulation. These results suggest that nanoliposomes are suitable for carrying fucoxanthin. Their incorporation into food matrices is critical to developing functional foods. Regulatory approvals and consumer perceptions regarding nanotechnology-based products must be addressed, emphasizing their safety and health benefits.
Keywords: enriched yogurt formulation; fucoxanthin-loaded nanoliposomes; functional foods.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rashwan A.K., Osman A.I., Chen W. Natural Nutraceuticals for Enhancing Yogurt Properties: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023;21:1907–1931. doi: 10.1007/s10311-023-01588-0. - DOI
-
- Almutairi B., Turner M.S., Fletcher M.T., Sultanbawa Y. The Impact of Commercial Prebiotics on the Growth, Survival and Nisin Production by Lactococcus lactis 537 in Milk. LWT. 2021;137:110356. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110356. - DOI
-
- González-Vega R.I., Robles-García M.Á., Mendoza-Urizabel L.Y., Cárdenas-Enríquez K.N., Ruiz-Cruz S., Gutiérrez-Lomelí M., Iturralde-García R.D., Avila-Novoa M.G., Villalpando-Vargas F.V., Del-Toro-Sánchez C.L. Impact of the ABO and RhD Blood Groups on the Evaluation of the Erythroprotective Potential of Fucoxanthin, β-Carotene, Gallic Acid, Quercetin and Ascorbic Acid as Therapeutic Agents against Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants. 2023;12:2092. doi: 10.3390/antiox12122092. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

