Structural basis for hepatitis E virus neutralization by potent human antibodies
- PMID: 40333967
- PMCID: PMC12057666
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adu8811
Structural basis for hepatitis E virus neutralization by potent human antibodies
Abstract
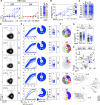
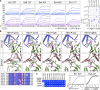
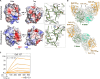
Antibodies targeting the hepatitis E virus (HEV) surface capsid protein (CA) are essential for infection control and resolution, yet their molecular and functional attributes remain largely elusive. We characterized 144 human HEV-CA-specific monoclonal antibodies cloned from the memory B cells of HEV-exposed individuals. Most human anti-CA antibodies cross-reacted with all HEV genotype variants, and a subset also recognized the zoonotic rat hepatitis E virus. HEV antibody repertoire was diverse and contained highly potent neutralizing antibodies binding to the CA protruding (P) domain. Structural analyses of CA protein complexed with three potent and broad HEV antibodies uncovered a neutralizing site located on monomeric P domain loops at the apex of the viral spike. These findings provide valuable insights into the protective humoral response to HEV and offer a framework for the rational design of HEV vaccines and immunotherapies.
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO), Hepatitis E. Fact sheet (WHO, 2023).
-
- Ma Z., de Man R. A., Kamar N., Pan Q., Chronic hepatitis E: Advancing research and patient care. J. Hepatol. 77, 1109–1123 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Kamar N., Izopet J., Pavio N., Aggarwal R., Labrique A., Wedemeyer H., Dalton H. R., Hepatitis E virus infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 3, 17086 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Wang Y., Zhao C., Qi Y., Geng Y., Hepatitis E virus. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1417, 1–13 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Geng Y., Shi T., Wang Y., Transmission of hepatitis E virus. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1417, 73–92 (2023). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

