Air traffic controller work state recognition based on improved xception network
- PMID: 40334013
- PMCID: PMC12057947
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0322404
Air traffic controller work state recognition based on improved xception network
Abstract
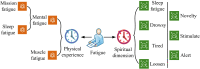
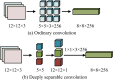
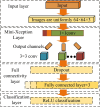
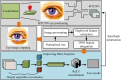
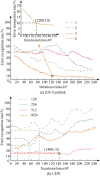
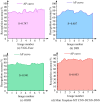
In the current context of rapid development of air traffic, the long-time and high-intensity working environment can easily lead to controllers' fatigue state, which in turn affects flight safety. Different from the traditional Mini-Xception pre-training network oriented to the classification task, the study improves it so that it can effectively process multi-dimensional time-series data of air traffic controllers' facial expressions and emotional changes. On its basis, a dynamic time-series data processing module is introduced and combined with a multi-task learning framework and a technique that combines multi-level feature extraction and emotional state analysis to realize the joint recognition of facial expressions and work states, such as fatigue and stress. The experiment findings denotes that the new model has the highest accuracy of 94.36% in detecting eye fatigue, the highest recall rate of 91.68%, and the maximum area under the curve test value of 93.02%. Compared to similar detection models, its average detection time is shortened by 1.9 seconds, with the highest accuracy of 95% in detecting 180 human eye images and an average fatigue detection of 91%. The innovation of the research is to utilize Mini-Xception network for real-time analysis of dynamic features of facial expressions and correlate them with the actual work performance of the controllers, which proposes a new multi-task learning framework, improves the accuracy and stability of the recognition, and provides a new idea and technical support for intelligent monitoring and control of air traffic management system.
Copyright: © 2025 Guo, Guan. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures






References
-
- Messeri C, Bicchi A, Zanchettin AM, Rocco P. A dynamic task allocation strategy to mitigate the human physical fatigue in collaborative robotics. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022;7(2):2178–85. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2022.3143520 - DOI
-
- Kamti MK, Iqbal R.Evolution of driver fatigue detection techniques-A review from 2007 to 2021. Transp. Res. Rec. 2022;2676(12):485–507. doi: 10.1177/03611981221096118 - DOI
-
- Zhang J, Wu Y, Chen Y, Wang J, Huang J, Zhang Q. Ubi-fatigue: toward ubiquitous fatigue detection via contactless sensing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022;9(15):14103–15. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3146942 - DOI
-
- Zhang Z,Ning H, Zhou F. A systematic survey of driving fatigue monitoring. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022;23(11):19999–20020. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2022.3189346.
-
- Zhu T, Zhang C, Wu T, Ouyang Z, Li H, Na X, Liang J, et al.. Research on a real-time driver fatigue detection algorithm based on facial video sequences. Appl. Sci. 2022;12(4):2224–5. doi: 10.3390/app12042224 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

