ADORE: an open platform study of ruxolitinib in combination with other novel therapies in patients with myelofibrosis
- PMID: 40334082
- PMCID: PMC12362515
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2025015860
ADORE: an open platform study of ruxolitinib in combination with other novel therapies in patients with myelofibrosis
Abstract
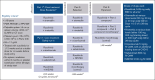
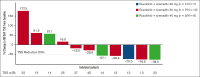
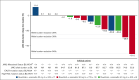
Ruxolitinib, a Janus kinase (JAK)1/JAK2 inhibitor, is the standard of care for symptomatic patients with myelofibrosis (MF). However, ∼70% of patients discontinue ruxolitinib after ∼5 years, a third of whom report suboptimal splenic response. ADORE was a phase 1b/2 study with an innovative open platform design that assessed the safety, efficacy, and pharmacokinetics of novel compounds in combination with ruxolitinib in patients with MF who had a suboptimal response to ruxolitinib alone. A total of 44 patients were enrolled in part 1 of the study of ruxolitinib in combination with siremadlin, rineterkib, sabatolimab, crizanlizumab, or NIS793. Most patients were allocated to receive ruxolitinib plus siremadlin (N = 23). The most frequent adverse events with siremadlin were gastrointestinal (nausea and diarrhea) and hematological (thrombocytopenia, anemia, and neutropenia). Siremadlin 30 mg orally once daily on days 1 to 5 of a 28-day cycle was selected as the recommended phase 2 dose. The most robust spleen volume reduction (SVR) at 24 weeks was observed with ruxolitinib plus siremadlin 30 mg. Reductions in percent JAK2V617F allele burden at week 24 were observed, notably in several patients with SVR. An increase in growth differentiation factor 15 protein levels in patients receiving siremadlin demonstrated the on-target modulation of downstream p53 targets. Overall, available data from ADORE suggest the feasibility and benefits of combining novel agents with ruxolitinib in patients with suboptimal response to ruxolitinib alone. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT04097821.
© 2025 American Society of Hematology. Published by Elsevier Inc. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: D.M.R. has received honoraria from Merck and Novartis, and has had an advisory role for Keros, Merck, Menarini, Novartis, and Takeda. F.H.H. has participated in advisory roles for Novartis, AOP Orphan, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), Merck, AbbVie, and Kartos, and received research funding from Novartis, BMS, and CTI BioPharma Corporation. A.C.P. has received consultation fees from Novartis and GSK, and honoraria from Novartis, CTI BioPharma Corporation, BMS, GSK, and AbbVie. A.R. reports receiving research support from AbbVie, AOP, AstraZeneca, Blueprint Medicines Corporation, BMS, Cogent Therapeutics LLC, GSK, Incyte, and Novartis; consultancy for AOP, Blueprint Medicines Corporation, GSK, and Novartis; honoraria for AOP, Blueprint Medicines Corporation, GSK, and Novartis; and travel reimbursement from AOP, Blueprint Medicines Corporation, GSK, and Novartis. H.B. received honoraria from Astellas, BMS, GSK, MSD, Novartis, and Servier. T.L. reports consultancy and advisory board participation for Novartis and AbbVie; and research funding from Novartis. O.V. reports receiving research funding and honoraria from Novartis. A.M.V. received fees from Novartis, Incyte, AbbVie, AOP, and GSK, and is on advisory boards for Novartis, Incyte, GSK, and AOP. V.G. reports institutional grants from AbbVie and Novartis; consulting fees from Novartis, BMS Celgene, GSK, AbbVie, Pfizer, and Daiichi Sankyo; honoraria from Novartis, BMS Celgene, and AbbVie; and participation on a data safety or advisory board for BMS Celgene, GSK, AbbVie, Pfizer, and Daiichi Sankyo. M. Wondergem reports participating in steering committee for Novartis; a data safety monitoring board for Keros therapeutics; and educational talks for Novartis and AOP. J.-J.K. reports consulting fees from GSK, Novartis, and AbbVie; honoraria from AOP Health and PharmaEssentia; support for attending meetings and/or travel from Novartis; and participation on a data safety monitoring board or advisory board for Incyte and BMS. G.C. is an employee of Novartis Ireland Limited, Dublin, Ireland. A.Z., A.P., and M. Wroclawska are employees of Novartis Pharma AG, Basel, Switzerland. J.K. is an employee and stockholder of Novartis Healthcare Pvt Ltd, Hyderabad, India. C.N.H. has received institutional grants from Constellation, GSK, and Novartis; received consultation fees from Novartis, MSD, Karyopharm, AOP, GSK, BMS, Sobi, Galecto, and CTI; received honoraria fees from Novartis, MSD, Karyopharm, Sobi, GSK, and BMS; received support for attending meetings and/or travel from Novartis; participated on a data safety monitoring board or advisory board for BMS and Galecto; leadership role with Blood Cancer UK (trustee; unpaid), European Hematology Association (Deputy Editor-in-Chief; remunerated), and MPN (myeloproliferative neoplasms) Voice (Medical Director; unpaid); and stock or stock options with Chakana Medical Limited. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
-
- Pemmaraju N, Bose P, Rampal R, Gerds AT, Fleischman A, Verstovsek S. Ten years after ruxolitinib approval for myelofibrosis: a review of clinical efficacy. Leuk Lymphoma. 2023;64(6):1063–1081. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

