Genetic biomarker study of sunvozertinib for clinical prognosis and prediction in NSCLC with EGFR exon 20 insertion mutation
- PMID: 40334661
- PMCID: PMC12147912
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.102121
Genetic biomarker study of sunvozertinib for clinical prognosis and prediction in NSCLC with EGFR exon 20 insertion mutation
Abstract
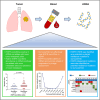
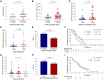
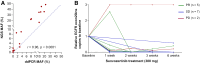
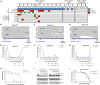
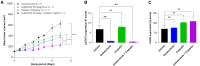
This is a report of biomarker analysis for sunvozertinib, a leading epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) targeting EGFR exon 20 insertion mutation (exon20ins) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). There is a positive correlation between positive EGFR exon20ins in plasma circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) and advanced disease. Shorter progression-free survival and lower objective response rate (45.8% vs. 68.0%) were observed in patients with positive EGFR exon20ins compared to those with negative status. Droplet digital PCR analysis showed that the EGFR exon20ins allele in ctDNA decreased over time in 85.7% of patients, with the earliest clearance occurred after 1 week of sunvozertinib treatment. Acquired EGFR C797S is identified as a potential on-target resistance mutation to sunvozertinib. Finally, efforts are undertaken to investigate therapeutic approaches that aim to overcome the putative acquired resistance to sunvozertinib.
Keywords: EGFR exon20ins; NSCLC; biomarker; sunvozertinib.
Copyright © 2025. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests Y.X. has received partial research funding from AstraZeneca outside the submitted work. J.C.-H.Y. reports institutional fees from Amgen for advisory works; grants, personal fees, and institutional fee from AstraZeneca for advisory works; institutional fee from Bayer for advisory works; institutional fees from Boehringer Ingelheim for advisory works; institutional fees from Bristol Myers Squibb for advisory works; institutional fee from Daiichi Sankyo for advisory works; institutional fee from Eli Lilly for advisory works; institutional fee from Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany, for advisory works; institutional fee from Merck Sharp & Dohme for advisory works; institutional fee from Novartis for advisory works; institutional fee from Pfizer for advisory works; grants and institutional fee from Roche/Genentech for advisory works; institutional fee and travel fee from Takeda Oncology for advisory works; institutional fee from Yuhan Pharmaceuticals for advisory works; institutional fee from Janssen Pharmaceuticals for advisory works; institutional fee from Gilead Sciences Inc., for advisory works; institutional fee from GSK for advisory works; personal fee from BeiGene for advisory works; institutional fee from Regeneron Pharmaceutical for advisory works; institutional fee from ArriVent for advisory works; institutional fee from AnHeart Therapeutics for advisory works; and travel fee from Dizal Pharmaceuticals to major conference. D.P. reports consulting, advisory role, or lectures: AstraZeneca, AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Janssen, Pfizer, Roche, Pierre Fabre, Takeda, ArriVent, Mirati, Seagen, and GSK; clinical trial research as a principal investigator or co-investigator (institutional financial interests): AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Medimmune, Sanofi-Aventis, Taiho Pharma, Novocure, Daiichi Sankyo, AbbVie, Janssen, Pierre Fabre, Takeda, ArriVent, Mirati, and Seagen; and travel, accommodations, and expenses: AstraZeneca, Roche, Novartis, and Pfizer. B.P.F. receives research support from Bristol Myers Squibb Foundation, Guardant Health, Bayer, Merck/MSD, Foundation Medicine, Illumina, Regeneron, AstraZeneca, Merus, Gilead, Catalyst, and OncoHost. E.F. reports receipt of personal honoraria for advisory board participation from AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, BMS, Daiichi Sankyo, F. Hoffmann-La Roche, Genmab, Gilead, GSK, ITeos Therapeutics, Janssen, Johnson & Johnson, MSD, Novartis, Pierre Fabre, Pfizer, Regeneron, Turning Point, and Daiichi Sankyo; personal speaker honoraria from Amgen, AstraZeneca, BMS, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, F. Hoffmann-La Roche, Johnson & Johnson, Genentech, Gilead, Janssen, Medical Trends, Medscape, Merck Serono, MSD, Novartis, PeerVoice, Pierre Fabre, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Touch Oncology; Board of Director role: Grifols; and financial support for meeting attendance and/or travel from AstraZeneca, Janssen, and Roche. E.F. is a principal investigator in trials (institutional financial support for clinical trials) sponsored by AstraZeneca, AbbVie, Amgen, Bayer, BeiGene, Boehringer Ingelheim, BMS, Daiichi Sankyo, Exelixis, F. Hoffmann-La Roche, Genentech, GSK, Janssen, MSD, Merck KGAA, Mirati, Novartis, Nuvalent, Pfizer, and Takeda. J.B.-B. reports personal fees from advisory boards (MSD and Roche); educational lectures from BMS, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Takeda, Regeneron, Amgen, Merck, and Sanofi, outside the submitted work; and has received support for attending meetings and/or travel from Takeda, MSD, and Roche. D.R.C.: Ad hoc consulting Dizal. L.B. has received consulting fees from Pfizer, AnHeart, AstraZeneca, Regeneron, Genentech, Janssen, Novocure, Bayer, Daichi, BMS, Sanofi, Gilead, Teligene, BI, BioAtla, and Neuvogen. M.N. is on the advisory board for AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Takeda, Novartis, EMD Serono, Janssen, Pfizer, Eli Lilly and Company, Bayer, Regeneron, BMS, and Genentech; a consultant for Caris Life Sciences (virtual tumor board); a speaker for Blueprint Medicines, Janssen, Mirati, and Takeda; reports travel support from AnHeart Therapeutics; and reports stock/stock options from MBrace Therapeutics. X.Z. and L.Z. are employees of Dizal Pharmaceutical and hold stock in Dizal Pharmaceutical. P.A.J.’s institution has received research funding from AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, PUMA, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Revolution Medicines, and Takeda Oncology. P.A.J. reports consulting fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, Roche/Genentech, Chugai Pharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly pharmaceuticals, SFJ Pharmaceuticals, Voronoi, Daiichi Sankyo, Biocartis, Novartis, Takeda Oncology, Mirati Therapeutics, Transcenta, Silicon Therapeutics, Syndax, Nuvalent, Bayer, Esai, Allorion Therapeutics, Accutar Biotech, AbbVie, Monte Rosa, Scorpion Therapeutics, Merus, Frontier Medicines, Hongyun Biotechnology, Duality, Blueprint Medicines, and Dizal Pharmaceuticals; stock in Gatekeeper Pharmaceuticals; and a patent for EGFR mutations issued, licensed, and with royalties paid by LabCorp.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sunvozertinib for patients in China with platinum-pretreated locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer and EGFR exon 20 insertion mutation (WU-KONG6): single-arm, open-label, multicentre, phase 2 trial.Lancet Respir Med. 2024 Mar;12(3):217-224. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00379-X. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Lancet Respir Med. 2024. PMID: 38101437 Clinical Trial.
-
Current clinical practice and physicians' insights on Chinese patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer habouring epidermal growth factor receptor 20 insertion mutation.BMC Cancer. 2024 Aug 23;24(1):1043. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12797-3. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39179992 Free PMC article.
-
Sunvozertinib monotherapy in EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor-resistant non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR mutations.Lung Cancer. 2025 Jan;199:108053. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2024.108053. Epub 2024 Dec 2. Lung Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39647463
-
Sunvozertinib: First Approval.Drugs. 2023 Nov;83(17):1629-1634. doi: 10.1007/s40265-023-01959-5. Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37962831 Review.
-
Targeted Therapies for EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutation in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 29;25(11):5917. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115917. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892105 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bauml J.M., Viteri S., Minchom A., Bazhenova L., Ou S., Schaffer M., Le Croy N., Riley R., Mahadevia P., Girard N. FP07.12 underdiagnosis of EGFR exon 20 insertion mutation variants: estimates from NGS-based real-world datasets. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021;16:S208–S209.
-
- Alix-Panabières C., Pantel K. Clinical Applications of Circulating Tumor Cells and Circulating Tumor DNA as Liquid Biopsy. Cancer Discov. 2016;6:479–491. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

