Genome-wide analyses of variance in blood cell phenotypes provide new insights into complex trait biology and prediction
- PMID: 40335489
- PMCID: PMC12059119
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-59525-4
Genome-wide analyses of variance in blood cell phenotypes provide new insights into complex trait biology and prediction
Abstract
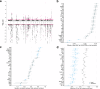
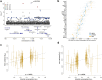
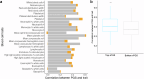
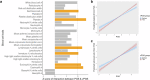
Blood cell phenotypes are routinely tested in healthcare to inform clinical decisions. Genetic variants influencing mean blood cell phenotypes have been used to understand disease aetiology and improve prediction; however, additional information may be captured by genetic effects on observed variance. Here, we mapped variance quantitative trait loci (vQTL), i.e. genetic loci associated with trait variance, for 29 blood cell phenotypes from the UK Biobank (N ~ 408,111). We discovered 176 independent blood cell vQTLs, of which 147 were not found by additive QTL mapping. vQTLs displayed on average 1.8-fold stronger negative selection than additive QTL, highlighting that selection acts to reduce extreme blood cell phenotypes. Variance polygenic scores (vPGSs) were constructed to stratify individuals in the INTERVAL cohort (N ~ 40,466), where the genetically most variable individuals had increased conventional PGS accuracy (by ~19%) relative to the genetically least variable individuals. Genetic prediction of blood cell traits improved by ~10% on average combining PGS with vPGS. Using Mendelian randomisation and vPGS association analyses, we found that alcohol consumption significantly increased blood cell trait variances highlighting the utility of blood cell vQTLs and vPGSs to provide novel insight into phenotype aetiology as well as improve prediction.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: M.I. is a trustee of the Public Health Genomics (PHG) Foundation, a member of the Scientific Advisory Board of Open Targets, and has research collaborations with AstraZeneca, Nightingale Health and Pfizer which are unrelated to this study. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Update of
-
Genome-wide analyses of variance in blood cell phenotypes provide new insights into complex trait biology and prediction.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 16:2024.04.15.24305830. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.15.24305830. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Commun. 2025 May 7;16(1):4260. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-59525-4. PMID: 38699308 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

