Predisposition to hematopoietic malignancies by deleterious germline CHEK2 variants
- PMID: 40335619
- PMCID: PMC12208901
- DOI: 10.1038/s41375-025-02635-1
Predisposition to hematopoietic malignancies by deleterious germline CHEK2 variants
Abstract
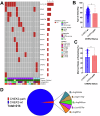
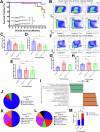
The role of germline CHEK2 variants in hematopoietic malignancies (HMs) is poorly understood. We examined pathogenic/likely pathogenic (P/LP) CHEK2 variants in patients with hereditary HMs (HHMs), a solid tumor risk cohort, public datasets, and a knock-in mouse model. In the HHM cohort, 57 probands had germline P/LP CHEK2 variants, mostly p.I157T (53%, 30/57). Among CHEK2 p.I157T carriers, 43% (19/44) had myeloid malignancies, 32% (14/44) had lymphoid malignancies, and 2% (1/44) had both. Among those with other germline P/LP CHEK2 alleles, 36% (13/36) had myeloid malignancies, 28% (10/36) had lymphoid malignancies, and 6% (2/36) had both. CHEK2 p.I157T was enriched in HM patients (OR 6.44, 95%CI 3.68-10.73, P < 0.001). In a solid tumor risk cohort, 36% (15/42) of CHEK2 p.I157T patients had a HM family history. A genome wide association study showed enrichment of CHEK2 loss-of-function variants with myeloid leukemia (P = 5.78e-7). In public acute myeloid leukemia (AML) datasets, 1% (16/1348) of patients had P/LP CHEK2 variants. In a public myelodysplastic neoplasms (MDS) dataset, 2% (5/214) had P/LP CHEK2 variants. Chek2 p.I161T mice, homologous to human p.I157T, had worse survival as heterozygotes (P = 0.037) or homozygotes (P = 0.005), with fewer Lin-CD34+ and Lin-cKit+ cells. Our data suggest P/LP CHEK2 variants are HHM risk alleles.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: RJS has received honoraria or participated on advisory boards from AbbVie, Jazz Pharamceuticals, Pfizer, Astellas, Kite/Gilead, BMS, and Sobi. He has received research funding from Jazz Pharmaceuticals. LAG receives royalties from UptoDate, Inc.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

