White matter hyperintensities, inflammation and cognitive impairments in drug-naïve first episode schizophrenia patients: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 40335945
- PMCID: PMC12060372
- DOI: 10.1186/s12888-025-06905-1
White matter hyperintensities, inflammation and cognitive impairments in drug-naïve first episode schizophrenia patients: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: Studies have reported that white matter hyperintensities (WMHs) are associated with disturbances in immune function, and the relationship between WMHs and cognitive impairments have been documented in various clinical populations. The present study was to examine the relationship between WMHs, immune function, and cognitive impairments in patients with schizophrenia (SCH) remains unknown.
Methods: A sample of 127 drug-naïve first episode SCH and 72 healthy controls (HCs) were included in this study. Serum levels of cytokines and oxidative stress indices were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and microtiter plate method. WMHs were assessed using T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging scanning, and cognitive performance was evaluated using the MATRICS Consensus Cognitive Battery.
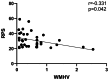
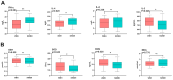
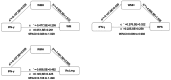
Results: We found patients with SCH are more likely to present with WMHs compared with HCs (OR = 2.076, 95%CI 1.007-4.277, p = 0.048). SCH with WMHs displayed more pronounced cognitive deficits in domains including speed of processing, working memory, verbal learning, visual learning, reasoning, and problem-solving compared with patients without WMHs (p < 0.05). Correlation analysis showed that the volume of WMHs was negative correlated with the problem-solving score (r=-0.331, p = 0.042) in patients with SCH. Within the SCH group, patients with WMHs exhibited elevated levels of interleukin-2 (IL-2), reactive oxygen species (ROS), and superoxide dismutase (SOD), along with lower levels of serum interleukin-4 (IL-4) and interferon-γ (IFN-γ) compared with those without WMHs (p < 0.05). The mediation analyses demonstrated that serum levels of IFN-γ in SCH had fully indirect effects on cognitive function, mediated by the WMHs.
Conclusions: This study suggests that WMHs may play a vital mediating role in the relationship between inflammation, oxidative stress, and cognitive impairments in SCH. Future studies exploring the potential clinical utility of WMHs as biomarkers for early detection and intervention of SCH are warranted.
Keywords: Cognitive impairments; Inflammation; Oxidative stress indices; Schizophrenia; White matter hyperintensities.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University (Approval No. 2019-KY-0271) provided full ethical approval for this study, and written informed consent was obtained from all study participants before investigation. All studies were conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, the Data Protection Act and other relevant guidelines and regulations. Written informed consent was obtained from all study participants and their parents or legal guardians. Consent for publication: The manuscript contains any information/images that the participant agrees to publish. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Associations between white matter hyperintensities, striatal dopamine loss, and cognition in drug-naïve Parkinson's disease.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2022 Apr;97:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2022.02.020. Epub 2022 Mar 3. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2022. PMID: 35276583
-
Glymphatic dysfunction mediates the influence of choroid plexus enlargement on information processing speed in patients with white matter hyperintensities.Cereb Cortex. 2024 Jun 4;34(6):bhae265. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhae265. Cereb Cortex. 2024. PMID: 38912605
-
Disturbed neurovascular coupling in patients with white matter hyperintensities: potential biomarker for cognitive impairment.Neuroradiology. 2024 Nov;66(11):1967-1978. doi: 10.1007/s00234-024-03459-z. Epub 2024 Dec 1. Neuroradiology. 2024. PMID: 39616265
-
Role of White Matter Hyperintensities and Related Risk Factors in Vascular Cognitive Impairment: A Review.Biomolecules. 2021 Jul 27;11(8):1102. doi: 10.3390/biom11081102. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34439769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research Progress in the Pathogenesis of Cognitive Dysfunction in White Matter Hyperintensities: A Narrative Review.J Integr Neurosci. 2025 Feb 19;24(2):24840. doi: 10.31083/JIN24840. J Integr Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40018769 Review.
References
-
- Leslie C. A systematic review of meta-analyses of the efficacy of oral atypical antipsychotics for the treatment of adult patients with schizophrenia. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2011;13(11). - PubMed
-
- Pérez-Iglesias R, et al. White matter integrity and cognitive impairment in First-Episode psychosis. Am J Psychiatry. 2010;167(4):451–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82201657/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- U21A20367/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 23210231104/Henan Province Science and Technology Research Project
- General Program of China Postdoctoral Science Foundation/General Program of China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
- LHGJ20220310/Henan Medical Science and Technology Research Program Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

